A double hit to kill tumor and endothelial cells by TRAIL and antiangiogenic 3TSR
- PMID: 19366809
- PMCID: PMC2981788
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2940
A double hit to kill tumor and endothelial cells by TRAIL and antiangiogenic 3TSR
Abstract
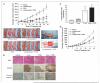
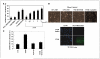
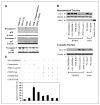
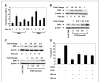
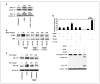
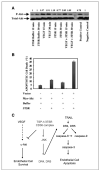
As tumor development relies on a coordination of angiogenesis and tumor growth, an efficient antitumor strategy should target both the tumor and its associated vessels. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces apoptosis in a tumor-selective manner. Additionally, thrombospondin-1, a naturally occurring inhibitor of angiogenesis, and a recombinant protein containing functional domains of thrombospondin-1, 3TSR, have been shown to be necessary and sufficient to inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Here, we show that a combination of a TRAIL receptor 2 agonist antibody, Lexatumumab, and 3TSR results in a significantly enhanced and durable tumor inhibition. We further observed that 3TSR induces apoptosis in primary endothelial cells by up-regulating the expression of TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 in a CD36 and Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase-dependent manner leading to the activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic machineries. The modulation of these pathways is critical for 3TSR-induced apoptosis as disrupting either via specific inhibitors reduced apoptosis. Moreover, 3TSR attenuates the Akt survival pathway. These studies indicate that 3TSR plays a critical role in regulating the proapoptotic signaling pathways that control growth and death in endothelial cells and that a combination of TRAIL and 3TSR acts as a double hit against tumor and tumor-associated vessels.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong LC, Bornstein P. Thrombospondins 1 and 2 function as inhibitors of angiogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2003;22:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Nor JE, Mitra RS, Sutorik MM, Mooney DJ, Castle VP, Polverini PJ. Thrombospondin-1 induces endothelial cell apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis by activating the caspase death pathway. J Vasc Res. 2000;37:209–18. - PubMed
-
- Stupack DG, Cheresh DA. Apoptotic cues from the extracellular matrix: regulators of angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2003;22:9022–9. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez B, Volpert OV, Crawford SE, Febbraio M, Silverstein RL, Bouck N. Signals leading to apoptosis-dependent inhibition of neovascularization by thrombospondin 1. Nat Med. 2000;6:41–8. - PubMed
-
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

