Hermes transposon distribution and structure in Musca domestica
- PMID: 19366812
- PMCID: PMC2877534
- DOI: 10.1093/jhered/esp017
Hermes transposon distribution and structure in Musca domestica
Abstract
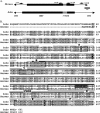
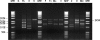
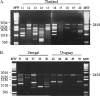
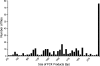
Hermes are hAT transposons from Musca domestica that are very closely related to the hobo transposons from Drosophila melanogaster and are useful as gene vectors in a wide variety of organisms including insects, planaria, and yeast. hobo elements show distinct length variations in a rapidly evolving region of the transposase-coding region as a result of expansions and contractions of a simple repeat sequence encoding 3 amino acids threonine, proline, and glutamic acid (TPE). These variations in length may influence the function of the protein and the movement of hobo transposons in natural populations. Here, we determine the distribution of Hermes in populations of M. domestica as well as whether Hermes transposase has undergone similar sequence expansions and contractions during its evolution in this species. Hermes transposons were found in all M. domestica individuals sampled from 14 populations collected from 4 continents. All individuals with Hermes transposons had evidence for the presence of intact transposase open reading frames, and little sequence variation was observed among Hermes elements. A systematic analysis of the TPE-homologous region of the Hermes transposase-coding region revealed no evidence for length variation. The simple sequence repeat found in hobo elements is a feature of this transposon that evolved since the divergence of hobo and Hermes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Hermes transposable element from the house fly, Musca domestica, is a short inverted repeat-type element of the hobo, Ac, and Tam3 (hAT) element family.Genet Res. 1994 Oct;64(2):87-97. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300032699. Genet Res. 1994. PMID: 7813905
-
Hermes, a functional non-Drosophilid insect gene vector from Musca domestica.Genetics. 1996 Mar;142(3):907-14. doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.3.907. Genetics. 1996. PMID: 8849896 Free PMC article.
-
The hobo transposable element of Drosophila can be cross-mobilized in houseflies and excises like the Ac element of maize.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9693-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9693. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8415764 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable elements and gene transformation in non-drosophilid insects.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Sep-Oct;26(8-9):739-53. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(96)00022-7. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 9014324 Review.
-
The hAT family: a versatile transposon group common to plants, fungi, animals, and man.Chromosoma. 2001 Apr;110(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s004120000118. Chromosoma. 2001. PMID: 11398971 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombination technologies for enhanced transgene stability in bioengineered insects.Genetica. 2011 Jan;139(1):71-8. doi: 10.1007/s10709-010-9494-4. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Genetica. 2011. PMID: 20844938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hosimary: a new hAT transposon group involved in horizontal transfer.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 May;283(5):451-9. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0531-x. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20339871
-
Transpositionally active episomal hAT elements.BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Dec 14;10:108. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-108. BMC Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 20003420 Free PMC article.
-
Hijacking Transposable Elements for Saturation Mutagenesis in Fungi.Front Fungal Biol. 2021 Apr 13;2:633876. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2021.633876. eCollection 2021. Front Fungal Biol. 2021. PMID: 37744130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transposable elements and xenobiotic resistance.Front Insect Sci. 2023 Jun 12;3:1178212. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2023.1178212. eCollection 2023. Front Insect Sci. 2023. PMID: 38469483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonnivard E, Bazin C, Denis B, Higuet D. A scenario for the hobo transposable element invasion, deduced from the structure of natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster using tandem TPE repeats. Genet Res. 2000;75:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Bonnivard E, Bazin C, Higuet D. High polymorphism of TPE repeats within natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster: a gradient of the 5TPE hobo element in Western Europe. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:2277–2284. - PubMed
-
- Bonnivard E, Higuet D, Bazin C. Characterization of natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster with regard to the hobo system: a new hypothesis on the invasion. Genet Res. 1997;69:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Boussy IA, Itoh M. Wanderings of hobo: a transposon in Drosophila melanogaster and its close relatives. Genetica. 2004;120:125–136. - PubMed

