In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase
- PMID: 19366835
- PMCID: PMC2798161
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2954
In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase
Abstract
Purpose: The mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway is important for cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation, and is frequently up-regulated in cancers. The MAP kinase pathway is also activated after exposure to ionizing radiation. We investigated the effects of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of MAP kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, on radiation response.
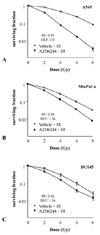
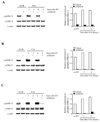
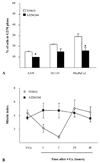
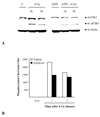
Experimental design: The effects of AZD6244 on the in vitro radiosensitivity of human cancer cell lines (A549, MiaPaCa2, and DU145) were evaluated using clonogenic assays. DNA damage repair was evaluated using gammaH2AX, and mitotic catastrophe was measured using nuclear fragmentation. Cell cycle effects were measured with flow cytometry. Growth delay was used to evaluate the effects of AZD6244 on in vivo tumor radiosensitivity.
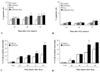
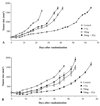
Results: Exposure of each cell line to AZD6244 before irradiation resulted in an increase in radiosensitivity with dose enhancement factors at a surviving fraction of 0.1, ranging from 1.16 to 2.0. No effects of AZD6244 on radiation-induced apoptosis or persistence of gammaH2AX foci after irradiation were detected. Cells treated with AZD6244 had an increased mitotic index and decreased Chk1 phosphorylation at 1 and 2 hours after irradiation. Mitotic catastrophe was increased in cells receiving AZD6244 and irradiation compared with the single treatments. In vivo studies revealed that AZD6244 administration to mice bearing A549 tumor xenografts resulted in a greater than additive increase in radiation-induced tumor growth delay (dose enhancement factor of 3.38).
Conclusions: These results indicate that AZD6244 can enhance tumor cell radiosensitivity in vitro and in vivo and suggest that this effect involves an increase in mitotic catastrophe.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) enhances the radiation responsiveness of lung and colorectal tumor xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 1;15(21):6619-29. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2958. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19843666
-
AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Aug;6(8):2209-19. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0231. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17699718
-
In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization induced by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.Neuro Oncol. 2013 Jul;15(7):880-90. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not030. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Neuro Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23519742 Free PMC article.
-
Combination treatment with MEK and AKT inhibitors is more effective than each drug alone in human non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 29;5(11):e14124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014124. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124782 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization induced by the DNA methylating agent temozolomide.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 1;14(3):931-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1856. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18245557
Cited by
-
Inhibition of MEK confers hypersensitivity to X-radiation in the context of BRAF mutation in a model of childhood astrocytoma.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015 Oct;62(10):1768-74. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25579. Epub 2015 May 15. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25981859 Free PMC article.
-
Selumetinib Activity in Thyroid Cancer Cells: Modulation of Sodium Iodide Symporter and Associated miRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 17;19(7):2077. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072077. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30018229 Free PMC article.
-
[Preclinical models in head and neck tumors : Evaluation of cellular and molecular resistance mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment].HNO. 2016 Dec;64(12):860-869. doi: 10.1007/s00106-016-0276-x. HNO. 2016. PMID: 27837212 Review. German.
-
Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor antagonizes paclitaxel in ovarian cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;16(2):600-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1979. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068074 Free PMC article.
-
Altering the response to radiation: radiosensitizers and targeted therapies in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: preclinical and emerging clinical evidence.Ann Pancreat Cancer. 2018 Aug;1(8):26. doi: 10.21037/apc.2018.08.02. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Ann Pancreat Cancer. 2018. PMID: 32656528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonner JA, Vroman BT, Christianson TJ, Karnitz LM. Ionizing radiation-induced MEK and Erk activation does not enhance survival of irradiated human squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42:921–925. - PubMed
-
- Kasid U, Suy S, Dent P, Ray S, Whiteside TL, Sturgill TW. Activation of Raf by ionizing radiation. Nature. 1996;382:813–816. - PubMed
-
- Sklar MD. The ras oncogenes increase the intrinsic resistance of NIH 3T3 cells to ionizing radiation. Science. 1988;239:645–647. - PubMed
-
- Bernhard EJ, Stanbridge EJ, Gupta S, et al. Direct evidence for the contribution of activated N-ras and K-ras oncogenes to increased intrinsic radiation resistance in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6597–6600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

