Plasma carboxy-terminal provasopressin (copeptin): a novel marker of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 19366852
- PMCID: PMC2708945
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-2278
Plasma carboxy-terminal provasopressin (copeptin): a novel marker of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Context: Stress-mediated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation, regulated by arginine vasopressin (AVP), may have a role in the pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome (MetSyn).
Objective: The objective of the study was to investigate whether plasma C-terminal provasopressin fragment (copeptin), a surrogate for circulating AVP, was associated with measures of insulin resistance and presence of MetSyn.
Design, setting, and participants: This was a multicenter, community-based study, investigating novel biomarkers for vascular disease. Participants included 1293 African-Americans (AA) (64 +/- 9 yr) and 1197 non-Hispanic whites (NHW) (59 +/- 10 yr) belonging to hypertensive sibships.
Main outcome measures: Plasma copeptin levels were measured by an immunoluminometric assay. MetSyn was defined per Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. Generalized estimating equations were used to assess whether plasma copeptin was associated with measures of insulin resistance and MetSyn.
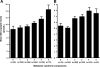
Results: The prevalence of MetSyn was 50% in AA and 49% in NHW. In each group, after adjustment for age and sex, plasma copeptin levels significantly correlated with body mass index, fasting plasma glucose and insulin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, triglycerides, and (inversely) high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (P < 0.05 for each variable). In multivariable logistic regression models that adjusted for age, sex, smoking, statin use, serum creatinine, education, physical activity, and diuretic use, plasma copeptin levels in the highest quartile were associated with an increased odds ratio of having MetSyn compared with bottom quartile: odds ratio (95% confidence interval) in AA, 2.07 (1.45-2.95); in NHW, 1.74 (1.21-2.5).
Conclusions: Our findings indicate a novel cross-sectional association between plasma copeptin and measures of insulin resistance and MetSyn.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum osteocalcin is associated with measures of insulin resistance, adipokine levels, and the presence of metabolic syndrome.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Jul;30(7):1474-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.204859. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20395593 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma copeptin, a unifying factor behind the metabolic syndrome.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jul;96(7):E1065-72. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-2981. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21490073
-
Copeptin and insulin resistance: effect modification by age and 11 β-HSD2 activity in a population-based study.J Endocrinol Invest. 2018 Jul;41(7):799-808. doi: 10.1007/s40618-017-0807-7. Epub 2017 Dec 12. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018. PMID: 29235050
-
Copeptin and its potential role in diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2013;23(2):172-90. doi: 10.11613/bm.2013.021. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2013. PMID: 23894863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copeptin as a novel biomarker of cardiometabolic syndrome.Endokrynol Pol. 2021;72(5):566-571. doi: 10.5603/EP.a2021.0072. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Endokrynol Pol. 2021. PMID: 34378786 Review.
Cited by
-
The association of copeptin with metabolic risk markers is modified by region of origin.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 10;13(1):19651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46908-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37949932 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressin and hydration play a major role in the development of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis in obese rats.Diabetologia. 2015 May;58(5):1081-90. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3496-9. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25622862
-
Neuroendocrine drivers of risk and resilience: The influence of metabolism & mitochondria.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2019 Jul;54:100770. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.100770. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31288042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of pre-meal water intake on the serum levels of Copeptin, glycemic control, lipid profile and anthropometric indices in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled trial.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Feb 1;20(1):171-177. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00724-9. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34178828 Free PMC article.
-
Association of HPA axis hormones with copeptin after psychological stress differs by sex.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016 Jan;63:254-61. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.10.009. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26520685 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Grundy SM 2008 Metabolic syndrome pandemic. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:629–636 - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM, Lithell H, Landsberg L 1996 Hypertension and associated metabolic abnormalities—the role of insulin resistance and the sympathoadrenal system. N Engl J Med 334:374–381 - PubMed
-
- Wang TJ, Larson MG, Keyes MJ, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS 2007 Association of plasma natriuretic peptide levels with metabolic risk factors in ambulatory individuals. Circulation 115:1345–1353 - PubMed
-
- Austin MA, Edwards KL 1996 Small, dense low density lipoproteins, the insulin resistance syndrome and noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Curr Opin Lipidol 7:167–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous