Elevated MBL concentrations are not an indication of association between the MBL2 gene and type 1 diabetes or diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 19366862
- PMCID: PMC2699850
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1495
Elevated MBL concentrations are not an indication of association between the MBL2 gene and type 1 diabetes or diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Objective: Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) is an essential component of the acute-phase immune response and may thus play a role in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. The serum concentration of MBL is mainly genetically determined, and elevated concentrations have been associated with both type 1 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Previous genetic studies have not been conclusive due to the small number of patients and polymorphisms studied. We investigated whether MBL2 polymorphisms are associated with type 1 diabetes or diabetic nephropathy and whether patients with nephropathy have elevated MBL concentrations as indicated previously. Furthermore, we studied the association between MBL2 polymorphisms and MBL concentration.
Research design and methods: We genotyped 20 MBL2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in a large, well-characterized Finnish case-control sample consisting of 1,297 patients with type 1 diabetes with or without nephropathy and 701 nondiabetic individuals. The serum concentration of MBL was available for 1,064 patients.
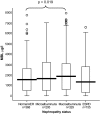
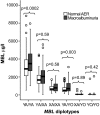
Results: We found that 19 SNPs were associated with the MBL concentration (P = 3 x 10(-81)-7 x 10(-4)). MBL concentrations were higher in patients with macroalbuminuria compared with patients without nephropathy even when the patients were stratified by the MBL2 genotypic background in accordance with previous studies. However, no evidence of association between any of the SNPs or their haplotype combinations and type 1 diabetes or diabetic nephropathy was observed.
Conclusions: Although most of the MBL2 SNPs studied were associated with the MBL concentration, no common variations (neither single SNPs nor their haplotype combinations) confer risk of type 1 diabetes or diabetic nephropathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of levels of mannose-binding lectin and the MBL2 gene with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e83059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083059. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376633 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes reverses elevated MBL levels in association with MBL2 genotype and VEGF expression.Diabetologia. 2016 Apr;59(4):853-8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3858-3. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26768002 Free PMC article.
-
Association between mannose-binding lectin and vascular complications in type 1 diabetes.Diabetes. 2004 Jun;53(6):1570-6. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.6.1570. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15161763
-
Mannose-binding lectin and MBL-associated serine protease-2 gene polymorphisms in a Brazilian population from Rio de Janeiro.Int J Immunogenet. 2012 Feb;39(1):32-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313X.2011.01052.x. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Int J Immunogenet. 2012. PMID: 22035380
-
Exercise and nutrition in type 1 diabetes: Insights from the FinnDiane cohort.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 22;13:1064185. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1064185. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36619534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation gene variants and susceptibility to albuminuria in the U.S. population: analysis in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III), 1991-1994.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Nov 5;11:155. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-155. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 21054877 Free PMC article.
-
The Complement Pathway: New Insights into Immunometabolic Signaling in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Oct;37(10-12):781-801. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0125. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34806406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Complement C5a Receptors in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8758. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108758. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common mechanisms underlying diabetic vascular complications: focus on the interaction of metabolic disorders, immuno-inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 30;21(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01016-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37904236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of levels of mannose-binding lectin and the MBL2 gene with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e83059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083059. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouwman LH, Eerligh P, Terpstra OT, Daha MR, de Knijff P, Ballieux BE, Bruining GJ, van der Slik AR, Roos A, Roep BO: Elevated levels of mannose-binding lectin at clinical manifestation of type 1 diabetes in juveniles. Diabetes 2005; 54: 3002– 3006 - PubMed
-
- Hansen TK, Thiel S, Knudsen ST, Gravholt CH, Christiansen JS, Mogensen CE, Poulsen PL: Elevated levels of mannan-binding lectin in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4857– 4861 - PubMed
-
- Saraheimo M, Teppo AM, Forsblom C, Fagerudd J, Groop PH: Diabetic nephropathy is associated with low-grade inflammation in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 1402– 1407 - PubMed
-
- Thiel S, Vorup-Jensen T, Stover CM, Schwaeble W, Laursen SB, Poulsen K, Willis AC, Eggleton P, Hansen S, Holmskov U, Reid KB, Jensenius JC: A second serine protease associated with mannan-binding lectin that activates complement. Nature 1997; 386: 506– 510 - PubMed
-
- Turner MW, Hamvas RM: Mannose-binding lectin: structure, function, genetics and disease associations. Rev Immunogenet 2000; 2: 305– 322 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

