Additional evidence that transaldolase exchange, isotope discrimination during the triose-isomerase reaction, or both occur in humans: effects of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 19366865
- PMCID: PMC2699876
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1300
Additional evidence that transaldolase exchange, isotope discrimination during the triose-isomerase reaction, or both occur in humans: effects of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether deuterium enrichment on carbons 5 and 3 (C5/C3) in plasma glucose is influenced by processes other than gluconeogenesis and, if so, whether these processes are altered by type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: In this study, 10 obese diabetic and 10 obese nondiabetic subjects were infused intravenously with [3,5-(2)H(2)] galactose enriched at a C5-to-C3 ratio of 1.0 as well as the enrichment of deuterium on C5 and C3 of plasma glucose, measured with nuclear magnetic resonance using the acetaminophen glucuronide method.
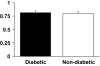
Results: The ratio of deuterium enrichment on C5 and C3 of glucose was <1 (P < 0.001) in all of the diabetic and nondiabetic subjects, resulting in a means +/- SE C5-to-C3 ratio that did not differ between groups (0.81 +/- 0.01 vs. 0.79 +/- 0.01, respectively).
Conclusions: That the C5-to-C3 glucose ratio is <1 indicates that transaldolase exchange, selective retention of deuterium at the level of the triose-isomerase reaction, or both occur in humans. This also indicates that the net effect of these processes on the C5-to-C3 ratio is the same in people with and without type 2 diabetes. The possible effects of transaldolase exchange or selective retention of deuterium (or tritium) at the level of the triose-isomerase reaction on tracee labeling and tracer metabolism should be considered when the deuterated water method is used to measure gluconeogenesis or [3-(3)H] glucose is used to measure glucose turnover in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Adkins A, Basu R, Persson M, Dicke B, Shah P, Vella A, Schwenk WF, Rizza R: Higher insulin concentrations are required to suppress gluconeogenesis than glycogenolysis in nondiabetic humans. Diabetes 2003; 52: 2213– 2220 - PubMed
-
- Basu R, Chandramouli V, Dicke B, Landau B, Rizza R: Obesity and type 2 diabetes impair insulin-induced suppression of glycogenolysis as well as gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1942– 1948 - PubMed
-
- Boden G, Chen X, Stein TP: Gluconeogenesis in moderately and severely hyperglycemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001; 280: E23– E30 - PubMed
-
- Gastaldelli A, Baldi S, Pettiti M, Toschi E, Camastra S, Natali A, Landau BR, Ferrannini E: Influence of obesity and type 2 diabetes on gluconeogenesis and glucose output in humans: a quantitative study. Diabetes 2000; 49: 1367– 1373 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

