Paraneoplastic antigen-like 5 gene (PNMA5) is preferentially expressed in the association areas in a primate specific manner
- PMID: 19366867
- PMCID: PMC2774394
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhp062
Paraneoplastic antigen-like 5 gene (PNMA5) is preferentially expressed in the association areas in a primate specific manner
Abstract
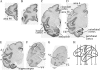
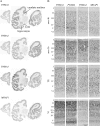
To understand the relationship between the structure and function of primate neocortical areas at a molecular level, we have been screening for genes differentially expressed across macaque neocortical areas by restriction landmark cDNA scanning (RLCS). Here, we report enriched expression of the paraneoplastic antigen-like 5 gene (PNMA5) in association areas but not in primary sensory areas, with the lowest expression level in primary visual cortex. In situ hybridization in the primary sensory areas revealed PNMA5 mRNA expression restricted to layer II. Along the ventral visual pathway, the expression gradually increased in the excitatory neurons from the primary to higher visual areas. This differential expression pattern was very similar to that of retinol-binding protein (RBP) mRNA, another association-area-enriched gene that we reported previously. Additional expression analysis for comparison of other genes in the PNMA gene family, PNMA1, PNMA2, PNMA3, and MOAP1 (PNMA4), showed that they were widely expressed across areas and layers but without the differentiated pattern of PNMA5. In mouse brains, PNMA1 was only faintly expressed and PNMA5 was not detected. Sequence analysis showed divergence of PNMA5 sequences among mammals. These findings suggest that PNMA5 acquired a certain specialized role in the association areas of the neocortex during primate evolution.
Figures






References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Amir Y, Harel M, Malach R. Cortical hierarchy reflected in the organization of intrinsic connections in macaque monkey visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1993;334:19–46. - PubMed
-
- Andersen RA. Visual and eye movement functions of the posterior parietal cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:377–403. - PubMed
-
- Baksh S, Tommasi S, Fenton S, Yu VC, Martins LM, Pfeifer GP, Latif F, Downward J, Neel BG. The tumor suppressor RASSF1A and MAP-1 link death receptor signaling to Bax conformational change and cell death. Mol Cell. 2005;18:637–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

