Lipid and insulin infusion-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance is likely due to metabolic feedback and not changes in IRS-1, Akt, or AS160 phosphorylation
- PMID: 19366875
- PMCID: PMC2711668
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90945.2008
Lipid and insulin infusion-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance is likely due to metabolic feedback and not changes in IRS-1, Akt, or AS160 phosphorylation
Abstract
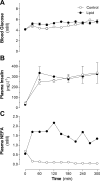
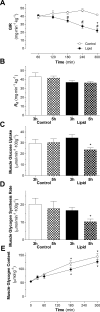
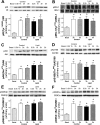
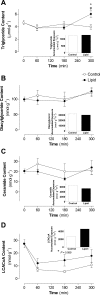
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by hyperlipidemia, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance. The aim of this study was to investigate whether acute hyperlipidemia-induced insulin resistance in the presence of hyperinsulinemia was due to defective insulin signaling. Hyperinsulinemia (approximately 300 mU/l) with hyperlipidemia or glycerol (control) was produced in cannulated male Wistar rats for 0.5, 1 h, 3 h, or 5 h. The glucose infusion rate required to maintain euglycemia was significantly reduced by 3 h with lipid infusion and was further reduced after 5 h of infusion, with no difference in plasma insulin levels, indicating development of insulin resistance. Consistent with this finding, in vivo skeletal muscle glucose uptake (31%, P < 0.05) and glycogen synthesis rate (38%, P < 0.02) were significantly reduced after 5 h compared with 3 h of lipid infusion. Despite the development of insulin resistance, there was no difference in the phosphorylation state of multiple insulin-signaling intermediates or muscle diacylglyceride and ceramide content over the same time course. However, there was an increase in cumulative exposure to long-chain acyl-CoA (70%) with lipid infusion. Interestingly, although muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 protein content was decreased in hyperinsulinemic glycerol-infused rats, this decrease was blunted in muscle from hyperinsulinemic lipid-infused rats. Decreased pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity was also observed in lipid- and insulin-infused animals (43%). Overall, these results suggest that acute reductions in muscle glucose metabolism in rats with hyperlipidemia and hyperinsulinemia are more likely a result of substrate competition than a significant early defect in insulin action or signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Alkhateeb H, Chabowski A, Glatz JF, Luiken JF, Bonen A. Two phases of palmitate-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle: impaired GLUT4 translocation is followed by a reduced GLUT4 intrinsic activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E783–E793, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Antinozzi PA, Segall L, Prentki M, McGarry JD, Newgard CB. Molecular or pharmacologic perturbation of the link between glucose and lipid metabolism is without effect on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. A re-evaluation of the long-chain acyl-CoA hypothesis. J Biol Chem 273: 16146–16154, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt BA, Dube JJ, Dedousis N, Reider JA, O'Doherty RM. Diet-induced obesity and acute hyperlipidemia reduce IκBα levels in rat skeletal muscle in a fiber-type dependent manner. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290: R233–R240, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bruce CR, Carey AL, Hawley JA, Febbraio MA. Intramuscular heat shock protein 72 and heme oxygenase-1 mRNA are reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes: evidence that insulin resistance is associated with a disturbed antioxidant defense mechanism. Diabetes 52: 2338–2345, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Chalkley SM, Hettiarachchi M, Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW. Five-hour fatty acid elevation increases muscle lipids and impairs glycogen synthesis in the rat. Metabolism 47: 1121–1126, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

