Pathogen recognition by innate immunity and its signaling
- PMID: 19367086
- PMCID: PMC3524297
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.85.143
Pathogen recognition by innate immunity and its signaling
Erratum in
- Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2009;85(6):216
Abstract
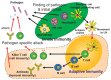
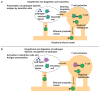
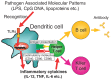
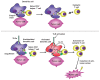
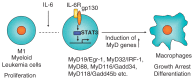
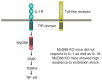
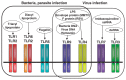
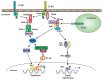
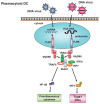
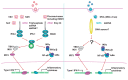
Mammalian immune response can be divided into innate and acquired immunity. Furthermore, much evidence has demonstrated that activation of innate immunity is a prerequisite to induction of acquired immunity. This paradigm shift has changed our thinking on the pathogenesis and treatment of infections, immune diseases, allergy, and cancers.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S., Uematsu S., Takeuchi O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 24, 783–801 - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X., Wei S., Matsuzaka T., et al. (1994) Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel ISGF3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 77, 63–71 - PubMed
-
- Muzio M., Ni J., Feng P., Dixit V.M. (1997) IRAK(Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 278, 1612–1615 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

