Influence of sequential guanidinium methylation on the energetics of the guanidinium...guanine dimer and guanidinium...guanine...cytosine trimer: implications for the control of protein...DNA interactions by arginine methyltransferases
- PMID: 19368013
- PMCID: PMC2929813
- DOI: 10.1021/jp808288p
Influence of sequential guanidinium methylation on the energetics of the guanidinium...guanine dimer and guanidinium...guanine...cytosine trimer: implications for the control of protein...DNA interactions by arginine methyltransferases
Abstract
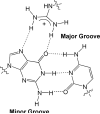
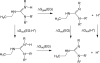
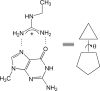
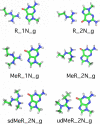
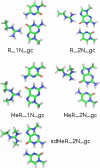
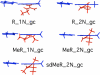
Arginine methylation is a post-translational protein modification that is catalyzed by proteins known as arginine methyl transferases (RMTs). Recently, arginine methylation was postulated as an important modification in modulating biomolecular interactions. RMTs largely target nuclear proteins, so it is highly likely that they aid in modulating protein...DNA interactions. In this study, we probe the influence that sequential guanidinium methylation has on the energetics of the guanidinium...guanine and guanidinium...guanine...cytosine complexes using ab initio and double-hybrid density functional theory (DFT) methods. Structures of guanidinium...guanine complexes derived at the MP2/6-31+G** level of theory show that monomethylated, symmetrically dimethylated, and unsymmetrical dimethylated guanidiniums are all capable of forming guanidinium...guanine complexes. However, when cytosine is involved in a base pair to guanine, only the monomethylated and symmetrically dimethylated guanidinium groups are capable of forming hydrogen bond complexes with guanine. At the B2-PLYP/6-311++G** level of theory, we found that methylation of the guanidinium group stabilizes the formation of the guanidinium... guanine complex relative to the unmethylated guanidinium...guanine complex by approximately 2.5 kcal mol(-1). The biological implication of these findings are discussed.
Figures



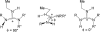


Similar articles
-
Non-covalent interactions: complexes of guanidinium with DNA and RNA nucleobases.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Oct 3;117(39):11608-16. doi: 10.1021/jp407339v. Epub 2013 Sep 19. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23992551
-
Mutual relationship between stacking and hydrogen bonding in DNA. Theoretical study of guanine-cytosine, guanine-5-methylcytosine, and their dimers.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Aug 12;114(31):10217-27. doi: 10.1021/jp103850h. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20684646
-
Base-pair interactions in the gas-phase proton-bonded complexes of C+G and C+GC.J Chem Phys. 2007 Dec 28;127(24):245102. doi: 10.1063/1.2817604. J Chem Phys. 2007. PMID: 18163711
-
State of the arg: protein methylation at arginine comes of age.Cell. 2001 Jul 13;106(1):5-8. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00423-8. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11461695 Review. No abstract available.
-
Methylation of the nuclear poly(A)-binding protein by type I protein arginine methyltransferases - how and why.Biol Chem. 2013 Aug;394(8):1029-43. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0121. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23412876 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of IKs channel-PIP2 interaction by PRMT1 plays a critical role in the control of cardiac repolarization.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jul;237(7):3069-3079. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30775. Epub 2022 May 17. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35580065 Free PMC article.
-
Protein arginine methylation facilitates KCNQ channel-PIP2 interaction leading to seizure suppression.Elife. 2016 Jul 28;5:e17159. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17159. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27466704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McBride AE, Silver PA. Cell. 2001;106:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Bedford MT, Richard S. Mol. Cell. 2005;18:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Bedford MT. J. Cell Science. 2007;120:4243–4246. - PubMed
-
- Pahlich S, Zakaryan RP, Gehring H. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1764:1890–1903. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Ma H, Hong H, Koh SS, Huang SM, Schurter BT, Aswad DW, Stallcup MR. Science. 1999;284:2174–2177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

