Loop diuretic use and rates of hip bone loss and risk of falls and fractures in older women
- PMID: 19368583
- PMCID: PMC2721719
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02195.x
Loop diuretic use and rates of hip bone loss and risk of falls and fractures in older women
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether loop diuretic use is associated with hip bone loss and greater risk of falls and fractures in older women.
Design: Prospective cohort study from August 1992 to April 2004.
Setting: Four regions in the United States from the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF).
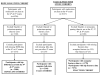
Participants: Women aged 65 and older (N=8,127) with medication use data who participated in the fourth SOF examination, from which three study cohorts were derived.
Measurements: Bone mineral density (BMD) of the total hip assessed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at the fourth and sixth examinations (n=2,980); recurrent (> or =2) falls in the year after the fourth examination (n=6,244); and incident fracture, including nonspine (n=6,778) and hip fracture (n=7,272).
Results: After multivariable adjustment, loop diuretic users had greater loss of total hip BMD than nonusers (mean annualized % BMD -0.87 vs -0.71, P=.03) after a mean of 4.4+/-0.6 years. The risks of recurrent falls (odds ratio=0.99, 95% confidence interval (CI)=0.71-1.39), nonspine (relative risk (RR)=1.04, 95% CI=0.90-1.21), and hip fracture (RR=1.03, 95% CI=0.81-1.31) were not greater in loop diuretic users than in nonusers.
Conclusion: In this cohort of older women, loop diuretic use was associated with a small but significantly higher rate of hip bone loss than nonuse after a mean duration of 4.4 years, although the risk of falls or fracture did not differ between the two groups.
Figures
References
-
- Anonymous Top 200 generic drugs by units in 2006. 2007. (Accessed at http://www.drugtopics.com/drugtopics/data/articlestandard//drugtopics/09....)
-
- Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Rosenberg L, et al. Recent patterns of medication use in the ambulatory adult population of the United States: the Slone survey. JAMA. 2002;287:337–344. - PubMed
-
- Rose BD. Diuretics. Kidney Int. 1991;39:336–352. - PubMed
-
- Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Pedersen AR, et al. Dose-effect relations of loop- and thiazide-diuretics on calcium homeostasis: A randomized, double-blinded Latin-square multiple cross-over study in postmenopausal osteopenic women. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003;33:41–50. - PubMed
-
- Ooms ME, Lips P, Van Lingen A, et al. Determinants of bone mineral density and risk factors for osteoporosis in healthy elderly women. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8:669–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR035583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR35582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035584/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG05394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R01 AG027574-22A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR35584/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R01 AG005394-22A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027576-22/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR35583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous