VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis
- PMID: 19369214
- PMCID: PMC2669337
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813061106
VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis
Abstract
VEGF-B, a homolog of VEGF discovered a long time ago, has not been considered an important target in antiangiogenic therapy. Instead, it has received little attention from the field. In this study, using different animal models and multiple types of vascular cells, we revealed that although VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth, it is critical for their survival. Importantly, the survival effect of VEGF-B is not only on vascular endothelial cells, but also on pericytes, smooth muscle cells, and vascular stem/progenitor cells. In vivo, VEGF-B targeting inhibited both choroidal and retinal neovascularization. Mechanistically, we found that the vascular survival effect of VEGF-B is achieved by regulating the expression of many vascular prosurvival genes via both NP-1 and VEGFR-1. Our work thus indicates that the function of VEGF-B in the vascular system is to act as a "survival," rather than an "angiogenic" factor and that VEGF-B inhibition may offer new therapeutic opportunities to treat neovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.N. and P.S. are employees of CSL Limited and A.N. holds stock options. R.J.W. and A.W.K. are employees of Genentech, Inc.
Figures
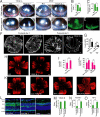
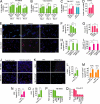

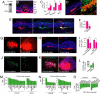
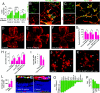
References
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005;438:967–974. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin LE, Hemo I, Keshet E. A plasticity window for blood vessel remodelling is defined by pericyte coverage of the preformed endothelial network and is regulated by PDGF-B and VEGF. Development (Cambridge, UK)t. 1998;125:1591–1598. - PubMed
-
- Makinen T, et al. Differential binding of vascular endothelial growth factor B splice and proteolytic isoforms to neuropilin-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21217–21222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

