Golden Rice is an effective source of vitamin A
- PMID: 19369372
- PMCID: PMC2682994
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.27119
Golden Rice is an effective source of vitamin A
Abstract
Background: Genetically engineered "Golden Rice" contains up to 35 microg beta-carotene per gram of rice. It is important to determine the vitamin A equivalency of Golden Rice beta-carotene to project the potential effect of this biofortified grain in rice-consuming populations that commonly exhibit low vitamin A status.
Objective: The objective was to determine the vitamin A value of intrinsically labeled dietary Golden Rice in humans.
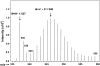
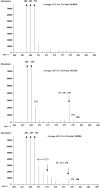
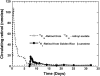
Design: Golden Rice plants were grown hydroponically with heavy water (deuterium oxide) to generate deuterium-labeled [2H]beta-carotene in the rice grains. Golden Rice servings of 65-98 g (130-200 g cooked rice) containing 0.99-1.53 mg beta-carotene were fed to 5 healthy adult volunteers (3 women and 2 men) with 10 g butter. A reference dose of [13C10]retinyl acetate (0.4-1.0 mg) in oil was given to each volunteer 1 wk before ingestion of the Golden Rice dose. Blood samples were collected over 36 d.
Results: Our results showed that the mean (+/-SD) area under the curve for the total serum response to [2H]retinol was 39.9 +/- 20.7 microg x d after the Golden Rice dose. Compared with that of the [13C10]retinyl acetate reference dose (84.7 +/- 34.6 microg x d), Golden Rice beta-carotene provided 0.24-0.94 mg retinol. Thus, the conversion factor of Golden Rice beta-carotene to retinol is 3.8 +/- 1.7 to 1 with a range of 1.9-6.4 to 1 by weight, or 2.0 +/- 0.9 to 1 with a range of 1.0-3.4 to 1 by moles.
Conclusion: Beta-carotene derived from Golden Rice is effectively converted to vitamin A in humans. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00680355.
Figures




Comment in
-
{beta}-Carotene from rice for human nutrition?Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Sep;90(3):695-6; author reply 696-7. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.28142. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19605569 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sommer A. Nutritional blindness: xerophthalmia and keratomalacia. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1982
-
- Ross AC, Stephensen CB. Vitamin A and retinoids in antiviral responses. FASEB J 1996;10:979–85 - PubMed
-
- Usha N, Sankaranarayanan A, Walia B, Ganguly N. Assessment of preclinical vitamin A deficiency in children with persistent diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1991;13:168–75 - PubMed
-
- Sommer A, West K., Jr Vitamin A deficiency. Health, survival, and vision. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1996
-
- Underwood BA, Arthur P. The contribution of vitamin A to public health. FASEB J 1996;10:1040–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

