Outcomes associated with race in males with nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 19369403
- PMCID: PMC2676182
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.06031108
Outcomes associated with race in males with nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: Blacks are over-represented among dialysis patients, but they have better survival rates than whites. It is unclear if the over-representation of blacks on dialysis is due to faster loss of kidney function or greater survival (or both) in predialysis stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
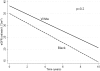
Design, setting, participants & measurements: We compared predialysis mortality, incidence of end stage renal disease (ESRD), and slopes of estimated GFR (eGFR) in 298 black versus 945 white male patients with moderate and advanced nondialysis-dependent CKD (NDD-CKD) from a single medical center. Mortality and ESRD incidence were compared in parametric survival models, and slopes of eGFR were assessed in mixed-effects models.
Results: Blacks had lower crude mortality and higher crude ESRD incidence. The lower mortality in blacks was explained by differences in case mix, especially a lower prevalence of cardiovascular disease, and the higher incidence of ESRD was explained by differences in case mix and baseline kidney function. The slopes of eGFR were similar in blacks and whites.
Conclusions: Lower mortality in black versus white patients is also observed in NDD-CKD and can be accounted for by differences in clinical characteristics. Higher mortality of black patients in earlier stages of CKD may result in the selection of a subgroup with fewer comorbidities and better survival in later stages of CKD. The higher crude ESRD rate in blacks appears to result from lower mortality in late stages of CKD, not faster progression of CKD.
Figures

References
-
- Easterling RE: Racial factors in the incidence and causation of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 23: 28–33, 1977 - PubMed
-
- Rostand SG, Kirk KA, Rutsky EA, Pate BA: Racial differences in the incidence of treatment for end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 306: 1276–1279, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Krop JS, Coresh J, Chambless LE, Shahar E, Watson RL, Szklo M, Brancati FL: A community-based study of explanatory factors for the excess risk for early renal function decline in blacks vs. whites with diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Arch Intern Med 159: 1777–1783, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Hsu CY, Lin F, Vittinghoff E, Shlipak MG: Racial differences in the progression from chronic renal insufficiency to end-stage renal disease in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 2902–2907, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AJ, Tell GS, Evans GW, Ettinger WH, Jr., Burkart JM: Survival of patients undergoing renal replacement therapy in one center with special emphasis on racial differences. Am J Kidney Dis 28: 72–81, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

