Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of lupus nephritis
- PMID: 19369404
- PMCID: PMC2678035
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008101028
Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of lupus nephritis
Abstract
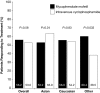
Recent studies have suggested that mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) may offer advantages over intravenous cyclophosphamide (IVC) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, but these therapies have not been compared in an international randomized, controlled trial. Here, we report the comparison of MMF and IVC as induction treatment for active lupus nephritis in a multinational, two-phase (induction and maintenance) study. We randomly assigned 370 patients with classes III through V lupus nephritis to open-label MMF (target dosage 3 g/d) or IVC (0.5 to 1.0 g/m(2) in monthly pulses) in a 24-wk induction study. Both groups received prednisone, tapered from a maximum starting dosage of 60 mg/d. The primary end point was a prespecified decrease in urine protein/creatinine ratio and stabilization or improvement in serum creatinine. Secondary end points included complete renal remission, systemic disease activity and damage, and safety. Overall, we did not detect a significantly different response rate between the two groups: 104 (56.2%) of 185 patients responded to MMF compared with 98 (53.0%) of 185 to IVC. Secondary end points were also similar between treatment groups. There were nine deaths in the MMF group and five in the IVC group. We did not detect significant differences between the MMF and IVC groups with regard to rates of adverse events, serious adverse events, or infections. Although most patients in both treatment groups experienced clinical improvement, the study did not meet its primary objective of showing that MMF was superior to IVC as induction treatment for lupus nephritis.
Figures
Comment in
-
[Is mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) better than intravenous cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of lupus nephritis?].Nefrologia. 2009;29(6 Suppl):40-2. doi: 10.3265/NEFROLOGIA.2009.29.S.E.noID.36.free. Nefrologia. 2009. PMID: 20221224 Spanish. No abstract available.
References
-
- Waldman M, Appel GB: Update on the treatment of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 70: 1403–1412, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Font J, Ramos-Casals M, Cervera R, García-Carrasco M, Torras A, Sisó A, Darnell A, Ingelmo M: Cardiovascular risk factors and the long-term outcome of lupus nephritis. QJM 94: 19–26, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Dooley MA, Hogan S, Jennette C, Falk R: Cyclophosphamide therapy for lupus nephritis: Poor renal survival in black Americans. Glomerular Disease Collaborative Network. Kidney Int 51: 1188–1195, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Barr RG, Seliger S, Appel GB, Zuniga R, D'Agati V, Salmon J, Radhakrishnan J: Prognosis in proliferative lupus nephritis: The role of socio-economic status and race/ethnicity. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18: 2039–2046, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Austin HA III, Klippel JH, Balow JE, le Riche NG, Steinberg AD, Plotz PH, Decker JL: Therapy of lupus nephritis: Controlled trial of prednisone and cytotoxic drugs. N Engl J Med 314: 614–619, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical