Nuclear fusion and genome encounter during yeast zygote formation
- PMID: 19369416
- PMCID: PMC2695800
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-12-1193
Nuclear fusion and genome encounter during yeast zygote formation
Abstract
When haploid cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are crossed, parental nuclei congress and fuse with each other. To investigate underlying mechanisms, we have developed assays that evaluate the impact of drugs and mutations. Nuclear congression is inhibited by drugs that perturb the actin and tubulin cytoskeletons. Nuclear envelope (NE) fusion consists of at least five steps in which preliminary modifications are followed by controlled flux of first outer and then inner membrane proteins, all before visible dilation of the waist of the nucleus or coalescence of the parental spindle pole bodies. Flux of nuclear pore complexes occurs after dilation. Karyogamy requires both the Sec18p/NSF ATPase and ER/NE luminal homeostasis. After fusion, chromosome tethering keeps tagged parental genomes separate from each other. The process of NE fusion and evidence of genome independence in yeast provide a prototype for understanding related events in higher eukaryotes.
Figures
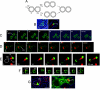
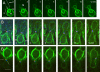
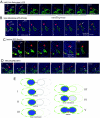
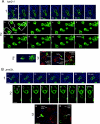


Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 20:2809.
Similar articles
-
Nuclear inner membrane fusion facilitated by yeast Jem1p is required for spindle pole body fusion but not for the first mitotic nuclear division during yeast mating.Genes Cells. 2008 Nov;13(11):1185-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01236.x. Genes Cells. 2008. PMID: 19090812
-
Distinct roles for key karyogamy proteins during yeast nuclear fusion.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(17):3773-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0163. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19570912 Free PMC article.
-
ER membrane-bending proteins are necessary for de novo nuclear pore formation.J Cell Biol. 2009 Mar 9;184(5):659-75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806174. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19273614 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear fusion in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:663-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.12.1.663. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996. PMID: 8970740 Review.
-
Big Lessons from Little Yeast: Budding and Fission Yeast Centrosome Structure, Duplication, and Function.Annu Rev Genet. 2017 Nov 27;51:361-383. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024733. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Annu Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28934593 Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed Encounter of Parental Genomes Can Lead to Aneuploidy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):139-151. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300289. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29150427 Free PMC article.
-
Flow cytometry-based purification of S. cerevisiae zygotes.J Vis Exp. 2012 Sep 21;(67):e4197. doi: 10.3791/4197. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 23023110 Free PMC article.
-
Uniting sex and eukaryote origins in an emerging oxygenic world.Biol Direct. 2010 Aug 23;5:53. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-53. Biol Direct. 2010. PMID: 20731852 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleolus as a polarized coaxial cable in which the rDNA axis is surrounded by dynamic subunit-specific phases.Curr Biol. 2021 Jun 21;31(12):2507-2519.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.03.041. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33862007 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of the cell nucleus, mitosis and sex: roles of intracellular coevolution.Biol Direct. 2010 Feb 4;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-7. Biol Direct. 2010. PMID: 20132544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baur T., Ramadan K., Schlundt A., Kartenbeck J., Meyer H. H. NSF- and SNARE-mediated membrane fusion is required for nuclear envelope formation and completion of nuclear pore complex assembly in Xenopus laevis egg extracts. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:2895–2903. - PubMed
-
- Beilharz T., Egan B., Silver P. A., Hofmann K., Lithgow T. Bipartite signals mediate subcellular targeting of tail-anchored membrane proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:8219–8223. - PubMed
-
- Bernales S., Papa F. R., Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;22:487–508. - PubMed
-
- Brandriff B. F., Gordon L. A., Segraves R., Pinkel D. The male-derived genome after sperm-egg fusion: spatial distribution of chromosomal DNA and paternal-maternal genomic association. Chromosoma. 1991;100:262–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

