Age and physical activity status effects on appetite and mood state in older humans
- PMID: 19370051
- PMCID: PMC4306339
- DOI: 10.1139/H08-150
Age and physical activity status effects on appetite and mood state in older humans
Abstract
This study examined the influences of age and chronic physical activity status on appetite and mood state. Groups of younger inactive, younger active, older inactive, and older active men and women completed questionnaires each waking hour, rating appetite and mood state for 1 day. Maximal oxygen consumption was 20% lower in older than in younger (p < 0.001) subjects, and 32% lower in inactive than in active (p < 0.001) subjects. Mean hunger (older, 4 +/- 1; younger, 5 +/- 1 arbitrary units (AU); p < 0.01) and desire to eat (older, 3 +/- 1; younger, 4 +/- 1 AU; p < 0.01) were lower in older than in younger subjects. Nadir arousal was higher for the active subjects (active, 3 +/- 1; inactive, 2 +/- 1 AU; p < 0.05). Nadir arousal, nadir pleasantness, and mean pleasantness were higher for the older subjects (p < 0.05). Physical activity status does not influence appetite or the age-associated declines in hunger or desire to eat. The increased nadir arousal of the physically active and older groups is consistent with these subjects experiencing less extreme sleepiness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors had no conflicts of interest.
Figures
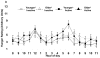
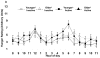



Similar articles
-
Food form and portion size affect postprandial appetite sensations and hormonal responses in healthy, nonobese, older adults.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 Feb;18(2):293-9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.217. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010. PMID: 19629055 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of Resistance Exercise on Appetite and Affect Following Pre-Sleep Feeding.Sports (Basel). 2018 Dec 11;6(4):172. doi: 10.3390/sports6040172. Sports (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544969 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary investigation of the effects of short-duration, vigorous exercise following sleep restriction, fragmentation and extension on appetite and mood in inactive, middle-aged men.J Sleep Res. 2021 Aug;30(4):e13215. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13215. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Sleep Res. 2021. PMID: 33111359 Clinical Trial.
-
Ageing Is Associated with Decreases in Appetite and Energy Intake--A Meta-Analysis in Healthy Adults.Nutrients. 2016 Jan 7;8(1):28. doi: 10.3390/nu8010028. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 26751475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in circulating appetite-related hormone concentrations between younger and older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020 Jul;32(7):1233-1244. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01292-6. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31432431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physical exercise practice was positively associated with better dietary practices of aged people during COVID-19 social distance: A cross-sectional study.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023 Apr;54:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.01.015. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023. PMID: 36963904 Free PMC article.
-
Does Habitual Physical Activity Increase the Sensitivity of the Appetite Control System? A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2016 Dec;46(12):1897-1919. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0518-9. Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 27002623 Free PMC article.
-
Does physical activity level and total energy expenditure relate to food intake, appetite, and body composition in healthy older adults? A cross-sectional study.Eur J Nutr. 2025 Jan 24;64(2):71. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03571-z. Eur J Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39853478 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between physical activity and appetite in patients with heart failure: A prospective observational study.Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2019 Jun;18(5):410-417. doi: 10.1177/1474515119836567. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30866679 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Exercise on Appetite in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 18;8:734267. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.734267. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34869516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellisle F. Food choice, appetite and physical activity. Public Health Nutr. 1999;2(3A):357–361. - PubMed
-
- Black AE. Critical evaluation of energy intake using the Goldberg cut-off for energy intake:basal metabolic rate. A practical guide to its calculation, use and limitations. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24(9):1119–1130. - PubMed
-
- Blundell JE, King NA. Physical activity and regulation of food intake: current evidence. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31(11 Suppl):S573–583. - PubMed
-
- Blundell JE, Stubbs RJ, Hughes DA, Whybrow S, King NA. Cross talk between physical activity and appetite control: does physical activity stimulate appetite? Proc Nutr Soc. 2003;62(3):651–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

