Cytoskeleton-membrane interactions in membrane raft structure
- PMID: 19370312
- PMCID: PMC2709161
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0022-6
Cytoskeleton-membrane interactions in membrane raft structure
Abstract
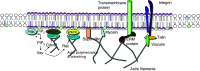
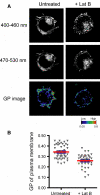
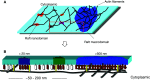
Cell membranes are structurally heterogeneous, composed of discrete domains with unique physical and biological properties. Membrane domains can form through a number of mechanisms involving lipid-lipid and protein-lipid interactions. One type of membrane domain is the cholesterol-dependent membrane raft. How rafts form remains a current topic in membrane biology. We review here evidence of structuring of rafts by the cortical actin cytoskeleton. This includes evidence that the actin cytoskeleton associates with rafts, and that many of the structural and functional properties of rafts require an intact actin cytoskeleton. We discuss the mechanisms of the actin-dependent raft organization, and the properties of the actin cytoskeleton in regulating raft-associated signaling events. We end with a discussion of membrane rafts and the actin cytoskeleton in T cell activation, which function synergistically to initiate the adaptive immune response.
Figures

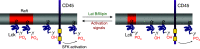
References
-
- Sharma P, Varma R, Sarasij RC, Ira, Gousset K, Krishnamoorthy G, Rao M, Mayor S (2004) Nanoscale organization of multiple GPI-anchored proteins in living cell membranes. Cell 116: 577–589 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

