A new low-field extremity magnetic resonance imaging and proposed compact MRI score: evaluation of anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics on rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19370385
- PMCID: PMC2720580
- DOI: 10.1007/s10165-009-0172-2
A new low-field extremity magnetic resonance imaging and proposed compact MRI score: evaluation of anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics on rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
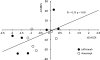
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful tool for evaluating disease activity and therapeutic efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, conventional whole-body MRI is inconvenient on several levels. We have therefore developed a new low-field extremity MRI (compact MRI, cMRI) and examined its clinical utility. Thirteen RA patients treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) biologics were included in the study. The MRI was performed twice using a 0.21-T extremity MRI system. The MRI images were scored using our proposed cMRI scoring system, which we devised with reference to the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials RA MRI score (OMERACT RAMRIS). In our cMRI scoring system, synovitis, bone edema, and bone erosion are separately graded on a scale from 0 to 3 by imaging over the whole hand, including the proximal interphalangeal joint. The total cMRI score (cMRIS) is then obtained by calculating the total bone erosion score x 1.5 + total bone edema score x 1.25 + total synovitis score. In this study, one patient showed a progression of bone destruction even under low clinical activity, as assessed by the disease activity score on 28 joints (DAS28); however, another patient's cMRIS decreased concurrently with the decrease in DAS28, with the positive correlation observed between DeltaDAS28 and DeltacMRIS (R = 0.055, P < 0.05). We conclude that cMRI and cMRIS are useful for assessing total disease activity and as a method linking MRI image evaluation to clinical evaluation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Response of early active rheumatoid arthritis to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging.Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(1):20-6. doi: 10.1007/s10165-008-0114-4. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Mod Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 18762862
-
Therapeutic efficacy of tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor-necrosis-factor inhibitors: 1 year follow-up with low-field extremity MRI.Mod Rheumatol. 2013 Jul;23(4):782-7. doi: 10.1007/s10165-012-0746-2. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Mod Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 22975733
-
Rapid reduction in tenosynovitis of the wrist and fingers evaluated by MRI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with etanercept.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jun;69(6):1117-22. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.116277. Epub 2010 May 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 20448287 Clinical Trial.
-
[Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor with infliximab or etanercept].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001 Sep 29;145(39):1880-5. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001. PMID: 11605312 Review. Dutch.
-
Role of biologics in early arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003 Sep-Oct;21(5 Suppl 31):S191-4. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14969075 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical interpretation of asymptomatic medial collateral ligament injury observed on magnetic resonance imaging in adolescent baseball players.Jpn J Radiol. 2017 Jun;35(6):319-326. doi: 10.1007/s11604-017-0636-9. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Jpn J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28421395
-
Influence of field strength, coil type and image resolution on assessment of synovitis by unenhanced MRI--a comparison with contrast-enhanced MRI.Eur Radiol. 2015 Apr;25(4):1059-67. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3470-9. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Eur Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25537977
-
Efficacy of tocilizumab on MRI-determined bone oedema in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;34(6):1031-7. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2934-x. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25903819
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17985417', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17985417/'}]}
- Cush JJ. Early rheumatoid arthritis—is there a window of opportunity? J Rheumatol Suppl. 2007;80:1–7. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/ard.59.7.521', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.59.7.521'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1753194', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1753194/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10873961', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10873961/'}]}
- Klarlund M, Ostergaard M, Jensen KE, Madsen JL, Skjødt H, Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: one year follow up of patients with early arthritis The TIRA Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59:521–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/ard.58.3.156', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.58.3.156'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1752839', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1752839/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10364913', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10364913/'}]}
- McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PL, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals progression of erosions despite clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58:156–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1186/ar794', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1186/ar794'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC193731', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC193731/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12932279', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12932279/'}]}
- Taylor PC. The value of sensitive imaging modalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5:210–3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1080/03009740310000058', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1080/03009740310000058'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12737323', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12737323/'}]}
- Ostergaard M, Szkudlarek M. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis—why MRI and ultrasonography can no longer be ignored. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32:63–73. - PubMed

