Molecular mechanisms of classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)
- PMID: 19370768
- PMCID: PMC3827857
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.21000
Molecular mechanisms of classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)
Abstract
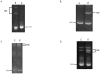
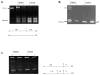
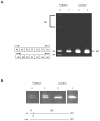
Classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a heritable disorder characterized by joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and abnormal wound healing. The majority of affected individuals have alterations in 1 of the 2 type V collagen genes, COL5A1 and COL5A2. The most common mechanism is COL5A1 haploinsufficiency due to instability of the transcript of one allele. In dermal fibroblasts from our population of 76 individuals with clinical features of classical EDS, there were 21 (29.5%) with decreased expression of one COL5A1 allele, consistent with published estimates of the frequency of null alleles. We identified the causative mutation in nine of these cell strains (mutations for seven others had been previously described), and found two nonsense mutations, five splice mutations, and two insertion/deletions. The same type of genomic change at splice sites can have different effects at the RNA level and the outcome could not be predicted from the primary genomic DNA alteration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Order of intron removal influences multiple splice outcomes, including a two-exon skip, in a COL5A1 acceptor-site mutation that results in abnormal pro-alpha1(V) N-propeptides and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Sep;71(3):451-65. doi: 10.1086/342099. Epub 2002 Jul 17. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12145749 Free PMC article.
-
Null alleles of the COL5A1 gene of type V collagen are a cause of the classical forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (types I and II).Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Jun;66(6):1757-65. doi: 10.1086/302933. Epub 2000 May 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10796876 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a patient with classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome due to a 9q34 duplication affecting COL5A1.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2018 Nov;58(6):191-193. doi: 10.1111/cga.12277. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2018. PMID: 29520887
-
Clinical and genetic aspects of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classic type.Genet Med. 2010 Oct;12(10):597-605. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181eed412. Genet Med. 2010. PMID: 20847697 Review.
-
Molecular genetics in classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2005 Nov 15;139C(1):17-23. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30070. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2005. PMID: 16278879 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Aspects in Shoulder Disorders.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020 Oct;55(5):537-542. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1702955. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 33093716 Free PMC article.
-
A Heterozygous Missense Variant in the COL5A2 in Holstein Cattle Resembling the Classical Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.Animals (Basel). 2020 Oct 30;10(11):2002. doi: 10.3390/ani10112002. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33143196 Free PMC article.
-
Novel COL5A1 variants and associated disease phenotypes in dogs with classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.J Vet Intern Med. 2024 Sep-Oct;38(5):2431-2443. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17180. Epub 2024 Aug 22. J Vet Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39175162 Free PMC article.
-
Heart valve development: regulatory networks in development and disease.Circ Res. 2009 Aug 28;105(5):408-21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.201566. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19713546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternative splicing of exon 64 in the COL5A1 gene.Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(3):267-76. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2011.636160. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Connect Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22149965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beighton P, De Paepe A, Steinmann B, Tsipouras P, Wenstrup RJ. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehers-Danlos Support Group (UK) Am J Med Genet. 1998;77:31–7. - PubMed
-
- Bonadio J, Holbrook KA, Gelinas RE, Jacob J, Byers PH. Altered triple helical structure of type I procollagen in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:1734–1742. - PubMed
-
- Byers PH, Schwarze U. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. In: Rimoin DL, Connor JM, Pyeritz RE, Korf B, editors. Emery and Rimoin’s Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics. Churchill Livingstone; London: 2002. pp. 4021–4043.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

