Hydrating for resistance to radicicol
- PMID: 19371133
- PMCID: PMC2843399
- DOI: 10.1021/cb9000712
Hydrating for resistance to radicicol
Abstract
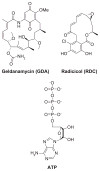
Resistance to Hsp90 inhibition has become an important concern as several clinical trials are currently in progress for the treatment of cancer. A summary of known mechanisms of resistance to Hsp90 inhibitors is provided, including the recent solution of the Humicola fuscoatra Hsp90 structure, the organism responsible for the biosynthesis of radicicol. Through careful analyses of Hsp90 structures, a plausible mechanism for resistance to Hsp90 inhibitors has been obtained by single mutations about the N-terminal ATP-binding site.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spotlight on the microbes that produce heat shock protein 90-targeting antibiotics.Open Biol. 2012 Dec 12;2(12):120138. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120138. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 23271830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geldanamycin, radicicol, and chimeric inhibitors of the Hsp90 N-terminal ATP binding site.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1173-82. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812031. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842154 Review.
-
The Hsp90 inhibitor radicicol interacts with the ATP-binding pocket of bacterial sensor kinase PhoQ.J Mol Biol. 2008 May 23;379(1):82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.036. Epub 2008 Mar 26. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18440021
-
Learning from nature: advances in geldanamycin- and radicicol-based inhibitors of Hsp90.J Org Chem. 2013 Jun 7;78(11):5117-41. doi: 10.1021/jo4002849. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Org Chem. 2013. PMID: 23496136
-
Design, synthesis, and structure--activity relationships for chimeric inhibitors of Hsp90.J Org Chem. 2006 Sep 29;71(20):7618-31. doi: 10.1021/jo061054f. J Org Chem. 2006. PMID: 16995666
Cited by
-
Hsp90 inhibition: elimination of shock and stress.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Sep 1;20(17):4983-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.108. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20656483 Free PMC article.
-
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hsp90.Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10(14):1380-402. doi: 10.2174/156802610792232088. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20536417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pearl LH, Prodromou C, Workman P. The Hsp90 molecular chaperone: an open and shut case for treatment. Biochem J. 2008;410:439–453. - PubMed
-
- Wanping X, Neckers L. Targeting the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 provides a multifaceted effect on diverse cell signaling pathways of cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1625–1629. - PubMed
-
- Prodromou C, Nuttall J, Millson S, Roe S, Pearl L, Workman P, Tiow-Suan S, Tan D, Piper P. The structural basis of the radicicol resistance displayed by a fungal Hsp90. ACS Chem Biol. 2009;4:289–297. - PubMed
-
- Benchekroun MN, Schneider E, Safa AR, Townsend AJ, Sinha BK. Mechanisms of resistance to ansamycin antibiotics in human breast cancer cells lines. Mol Pharmacol. 1994;46:677–684. - PubMed
-
- Madden TA, Pumford S, Barrow D, Dutkowski CM, McClelland R, Nicholson RI. Development of acquired resistance to 17(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) in hormone refractory breast cancers in vitro. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2005;46 Abstract LB-267.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

