Morphine is an arteriolar vasodilator in man
- PMID: 19371311
- PMCID: PMC2679101
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03364.x
Morphine is an arteriolar vasodilator in man
Abstract
Aim: The mechanisms of action of morphine on the arterial system are not well understood. The aim was to report forearm vascular responses, and their mediation, to intra-arterial morphine in healthy subjects.
Methods: Three separate protocols were performed: (i) dose ranging; (ii) acute tolerance; (iii) randomized crossover mechanistic study on forearm blood flow (FBF) responses to intrabrachial infusion of morphine using venous occlusion plethysmography. Morphine was infused either alone (study 1 and 2), or with an antagonist: naloxone, combined histamine-1 and histamine-2 receptor blockade or during a nitric oxide clamp.
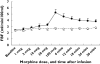
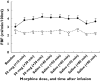
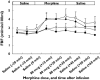
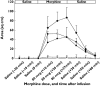
Results: Morphine caused an increase in FBF at doses of 30 microg min(-1)[3.25 (0.26) ml min(-1) 100 ml(-1)][mean (SEM)] doubling at 100 microg min(-1) to 5.23 (0.53) ml min(-1) 100 ml(-1). Acute tolerance was not seen to 50 microg min(-1) morphine, with increased FBF [3.96 (0.35) ml min(-1) 100 ml(-1)] (P = 0.003), throughout the 30-min infusion period. Vasodilatation was abolished by pretreatment with antihistamines (P = 0.008) and the nitric oxide clamp (P < 0.001), but not affected by naloxone. The maximum FBF with pretreatment with combined H1/H2 blockade was 3.06 (0.48) and 2.90 (0.17) ml min(-1) 100 ml(-1) after 30 min, whereas with morphine alone it reached 4.3 (0.89) ml min(-1) 100 ml(-1).
Conclusions: Intra-arterial infusion of morphine into the forearm circulation causes vasodilatation through local histamine-modulated nitric oxide release. Opioid receptor mechanisms need further exploration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histamine-induced vasodilatation in the human forearm vasculature.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;76(5):699-707. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12110. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23488545 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Endothelial release of nitric oxide contributes to the vasodilator effect of adenosine in humans.Circulation. 1995 Oct 15;92(8):2135-41. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.8.2135. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7554193
-
Activation of the ATP-dependent potassium channel attenuates norepinephrine-induced vasoconstriction in the human forearm.Shock. 2004 Oct;22(4):320-5. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000142250.85264.10. Shock. 2004. PMID: 15377886 Clinical Trial.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced vasodilation in the human forearm is antagonized by CGRP8-37: evaluation of a human in vivo pharmacodynamic model.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Mar;79(3):263-73. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.11.005. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16513450 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra-arterial substance P mediated vasodilatation in the human forearm: pharmacology, reproducibility and tolerability.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997 May;43(5):493-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1997.00583.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9159564 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Pain and Analgesic Medications on Blood Pressure.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022 Oct;24(10):385-394. doi: 10.1007/s11906-022-01205-5. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022. PMID: 35704141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-dose morphine reduces pain perception and blood pressure, but not muscle sympathetic outflow, responses during the cold pressor test.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Jul 1;323(1):H223-H234. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00092.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35714174 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Perspectives and Management of Edema in Chronic Venous Disease-What about Ruscus?Medicines (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;9(8):41. doi: 10.3390/medicines9080041. Medicines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic profiles associated with opioid use and opioid use disorder: a narrative review of the literature.Curr Addict Rep. 2023 Sep;10(3):581-593. doi: 10.1007/s40429-023-00493-4. Epub 2023 May 19. Curr Addict Rep. 2023. PMID: 37982033 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of individual and treatment characteristics on wearable sensor-based digital biomarkers of opioid use.NPJ Digit Med. 2022 Aug 22;5(1):123. doi: 10.1038/s41746-022-00664-z. NPJ Digit Med. 2022. PMID: 35995825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fahmy NR, Sunder N, Soter NA. Role of histamine in the hemodynamic and plasma catecholamine responses to morphine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983;33:615–20. - PubMed
-
- Petry NM, Bickel WK, Huddleston J, Tzanis E, Badger GJ. A comparison of subjective, psychomotor and physiological effects of a novel muscarinic analgesic, LY297802 tartrate, and oral morphine in occasional drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998;50:129–36. - PubMed
-
- Lowenstein E, Hallowell P, Levine FH, Daggett WM, Austen WG, Laver MB. Cardiovascular response to large doses of intravenous morphine in man. N Engl J Med. 1969;281:1389–93. - PubMed
-
- Mildh LH, Tuomisto LM, Scheinin M, Kirvela OA. Morphine-induced cardiovascular stimulation: the effects of two doses on healthy subjects. Anesth Analg. 2000;91:51–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

