Zoledronic acid induces formation of a pro-apoptotic ATP analogue and isopentenyl pyrophosphate in osteoclasts in vivo and in MCF-7 cells in vitro
- PMID: 19371349
- PMCID: PMC2707989
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00160.x
Zoledronic acid induces formation of a pro-apoptotic ATP analogue and isopentenyl pyrophosphate in osteoclasts in vivo and in MCF-7 cells in vitro
Abstract
Background and purpose: Bisphosphonates (BPs) are highly effective inhibitors of bone resorption. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (N-BPs), such as zoledronic acid, induce the formation of a novel ATP analogue (1-adenosin-5'-yl ester 3-(3-methylbut-3-enyl) ester triphosphoric acid; ApppI), as a consequence of the inhibition of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and the accumulation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP). ApppI induces apoptosis, as do comparable metabolites of non-nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (non-N-BPs). In order to further evaluate a pharmacological role for ApppI, we obtained more detailed data on IPP/ApppI formation in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, zoledronic acid-induced ApppI formation from IPP was compared with the metabolism of clodronate (a non-N-BP) to adenosine 5'(beta,gamma-dichloromethylene) triphosphate (AppCCl2p).
Experimental approach: After giving zoledronic acid in vivo to rabbits, IPP/ApppI formation and accumulation was assessed in isolated osteoclasts. The formation of ApppI from IPP was compared with the metabolism of clodronate in MCF-7 cells in vitro. IPP/ApppI and AppCCl2p levels in cell extracts were analysed by mass spectrometry.
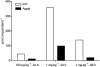
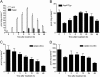
Key results: Isopentenyl pyrophosphate/ApppI were formed in osteoclasts in vivo, after a single, clinically relevant dose of zoledronic acid. Furthermore, exposure of MCF-7 cells in vitro to zoledronic acid at varying times and concentrations induced time- and dose-dependent accumulation of IPP/ApppI. One hour pulse treatment was sufficient to cause IPP accumulation and subsequent ApppI formation, or the metabolism of clodronate into AppCCl2p.
Conclusions and implications: This study provided the first conclusive evidence that pro-apoptotic ApppI is a biologically significant molecule, and demonstrated that IPP/ApppI analysis is a sensitive tool for investigating pathways involved in BP action.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Zoledronic acid-induced IPP/ApppI production in vivo.Life Sci. 2007 Sep 8;81(13):1066-70. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17850825
-
Bisphosphonate-induced ATP analog formation and its effect on inhibition of cancer cell growth.Anticancer Drugs. 2008 Apr;19(4):391-9. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3282f632bf. Anticancer Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18454049
-
The level of ATP analog and isopentenyl pyrophosphate correlates with zoledronic acid-induced apoptosis in cancer cells in vitro.Bone. 2009 Dec;45(6):1153-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.08.010. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19699819
-
Bisphosphonates: the first 40 years.Bone. 2011 Jul;49(1):2-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.04.022. Epub 2011 May 1. Bone. 2011. PMID: 21555003 Review.
-
The molecular basis of bisphosphonate activity: a preclinical perspective.Semin Oncol. 2010 Jun;37 Suppl 1:S3-11. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.06.003. Semin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20682369 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone-seeking nanoplatform co-delivering cisplatin and zoledronate for synergistic therapy of breast cancer bone metastasis and bone resorption.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Dec;10(12):2384-2403. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33354509 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic acid induces apoptosis and S-phase arrest in mesothelioma through inhibiting Rab family proteins and topoisomerase II actions.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Nov 13;5(11):e1517. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.475. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25393473 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effect of zoledronic acid on human vascular smooth muscle cells.J Surg Res. 2013 Jun 15;182(2):339-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.033. Epub 2012 Nov 8. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23164362 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic acid induces apoptosis and autophagy in cervical cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2014 Dec;35(12):11913-20. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2460-5. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25142231
-
Low-intensity continuous ultrasound triggers effective bisphosphonate anticancer activity in breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 18;5:16354. doi: 10.1038/srep16354. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26578234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin D, Cornell SA, Gustafson SK, Needle SJ, Ullrich JW, Bilder GE, et al. Bisphosphonates used for the treatment of bone disorders inhibit squalene synthase and cholesterol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 1992;33:1657–1663. - PubMed
-
- Auriola S, Frith J, Rogers MJ, Koivuniemi A, Mönkkönen J. Identification of adenine nucleotide-containing metabolites of bisphosphonate drugs using ion-pair liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997;704:187–195. - PubMed
-
- Benford HL, Frith JC, Auriola S, Mönkkönen J, Rogers MJ. Farnesol and geranylgeraniol prevent activation of caspases by aminobisphosphonates: biochemical evidence for two distinct pharmacological classes of bisphosphonate drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980;21:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Coleman RE. The role of bisphosphonates in breast cancer. Breast. 2004;13(Suppl.)(1):S19–S28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

