Combining a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alogliptin, with pioglitazone improves glycaemic control, lipid profiles and beta-cell function in db/db mice
- PMID: 19371350
- PMCID: PMC2707988
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00145.x
Combining a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alogliptin, with pioglitazone improves glycaemic control, lipid profiles and beta-cell function in db/db mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Alogliptin, a highly selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, enhances incretin action and pioglitazone enhances hepatic and peripheral insulin actions. Here, we have evaluated the effects of combining these agents in diabetic mice.
Experimental approach: Effects of short-term treatment with alogliptin alone (0.01%-0.1% in diet), and chronic combination treatment with alogliptin (0.03% in diet) and pioglitazone (0.0075% in diet) were evaluated in db/db mice exhibiting early stages of diabetes.
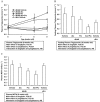
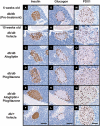
Key results: Alogliptin inhibited plasma DPP-4 activity up to 84% and increased plasma active glucagon-like peptide-1 by 4.4- to 4.9-fold. Unexpectedly, alogliptin alone lacked clear efficacy for improving glucose levels. However, alogliptin in combination with pioglitazone clearly enhanced the effects of pioglitazone alone. After 3-4 weeks of treatment, combination treatment increased plasma insulin by 3.8-fold, decreased plasma glucagon by 41%, both of which were greater than each drug alone, and increased plasma adiponectin by 2.4-fold. In addition, combination treatment decreased glycosylated haemoglobin by 2.2%, plasma glucose by 52%, plasma triglycerides by 77% and non-esterified fatty acids by 48%, all of which were greater than each drug alone. Combination treatment also increased expression of insulin and pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (PDX1), maintained normal beta-cell/alpha-cell distribution in islets and restored pancreatic insulin content to levels comparable to non-diabetic mice.
Conclusions and implications: These results indicate that combination treatment with alogliptin and pioglitazone at an early stage of diabetes improved metabolic profiles and indices that measure beta-cell function, and maintained islet structure in db/db mice, compared with either alogliptin or pioglitazone monotherapy.
Figures
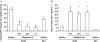




Similar articles
-
The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in combination with pioglitazone improves glycemic control, lipid profiles, and increases pancreatic insulin content in ob/ob mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan 14;602(2-3):448-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.11.017. Epub 2008 Nov 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19038243
-
Pioglitazone and alogliptin combination therapy in type 2 diabetes: a pathophysiologically sound treatment.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010 Sep 7;6:671-90. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s4852. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010. PMID: 20859539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic administration of alogliptin, a novel, potent, and highly selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, improves glycemic control and beta-cell function in obese diabetic ob/ob mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul 7;588(2-3):325-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.04.018. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18499100
-
Combination treatment with alogliptin and voglibose increases active GLP-1 circulation, prevents the development of diabetes and preserves pancreatic beta-cells in prediabetic db/db mice.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010 Mar;12(3):224-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01156.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. PMID: 20151999
-
Alogliptin: A new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014 Jan 15;71(2):103-9. doi: 10.2146/ajhp130131. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24375601 Review.
Cited by
-
Potent antiatherosclerotic effects of alogliptin in addition to its potent antidiabetic effects.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012;5:121-3. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S31889. Epub 2012 May 11. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012. PMID: 22654521 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lowering of postprandial lipids in individuals with type 2 diabetes treated with alogliptin and/or pioglitazone: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study.Diabetologia. 2012 Apr;55(4):915-25. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2447-3. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22237690 Clinical Trial.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes: safety, tolerability, and efficacy.Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2010;2:7-19. doi: 10.2147/dhps.s6270. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2010. PMID: 21701614 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study.Diabetes Metab J. 2022 Sep;46(5):689-700. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0183. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Diabetes Metab J. 2022. PMID: 35295073 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute DPP-4 inhibition modulates vascular tone through GLP-1 independent pathways.Vascul Pharmacol. 2011 Jul-Sep;55(1-3):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21397040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cejvan K, Coy DH, Efendic S. Intra-islet somatostatin regulates glucagon release via type 2 somatostatin receptors in rats. Diabetes. 2003;52(5):1176–1181. - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A. The possible role of postprandial hyperglycaemia in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetologia. 2003;46(Suppl.)(1):M9–M16. - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A, Johns D, Widel M, Eckland DJ, Gilmore KJ, Tan MH. Comparison of effect of pioglitazone with metformin or sulfonylurea (monotherapy and combination therapy) on postload glycaemia and composite insulin sensitivity index during an oral glucose tolerance test in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(2):266–272. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier G. Oral combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18(Suppl.)(3):S70–S76. - PubMed
-
- Deacon CF. Therapeutic strategies based on glucagon-like peptide 1. Diabetes. 2004;53(9):2181–2189. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

