Galectins and gliomas
- PMID: 19371355
- PMCID: PMC2805916
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00270.x
Galectins and gliomas
Abstract
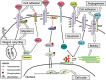
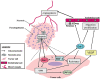
Malignant gliomas, especially glioblastomas, are associated with a dismal prognosis. Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, glioblastoma patients still have a median survival expectancy of only 14 months. This poor prognosis can be at least partly explained by the fact that glioma cells diffusely infiltrate the brain parenchyma and exhibit decreased levels of apoptosis, and thus resistance to cytotoxic drugs. Galectins are a family of mammalian beta-galactoside-binding proteins characterized by a shared characteristic amino acid sequence. They are expressed differentially in normal vs. neoplastic tissues and are known to play important roles in several biological processes such as cell proliferation, death and migration. This review focuses on the role played by galectins, especially galectin-1 and galectin-3, in glioma biology. The involvement of these galectins in different steps of glioma malignant progression such as migration, angiogenesis or chemoresistance makes them potentially good targets for the development of new drugs to combat these malignant tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Aplin AE, Howe AK, Juliano RL (1999) Cell adhesion molecules, signal transduction and cell growth. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:737–744. - PubMed
-
- Barondes SH, Castronovo V, Cooper DN, Cummings RD, Drickamer K, Feizi T et al (1994) Galectins: a family of animal beta‐galactoside‐binding lectins. Cell 76:597–598. - PubMed
-
- Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H (1994) Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem 269:20807–20810. - PubMed
-
- Bartik P, Maglott A, Entlicher G, Vestweber D, Takeda K, Martin S, Dontenwill M (2008) Detection of a hypersialylated beta1 integrin endogenously expressed in the human astrocytoma cell line A172. Int J Oncol 32:1021–1031. - PubMed
-
- Bellail AC, Hunter SB, Brat DJ, Tan C, Van Meir EG (2004) Microregional extracellular matrix heterogeneity in brain modulates glioma cell invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1046–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

