Mortality in human sepsis is associated with downregulation of Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 expression on blood monocytes
- PMID: 19371402
- PMCID: PMC2672063
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-4-12
Mortality in human sepsis is associated with downregulation of Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 expression on blood monocytes
Abstract
Pattern recognition receptors are a key component of the first line host defense against infection, recognizing specific microbial products. We hypothesize that monocyte hyporesponsiveness in human sepsis is associated with a downregulation of the pattern recognition receptors Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR4.Protein expression of CD14, TLR2 and TLR4 on blood monocytes was examined using flow cytometry from 29 patients with sepsis and 14 healthy controls. In addition LPS stimulated TNF-alpha and IL-10 production was studied in a 24 hour whole blood assay.We found an increased expression of CD14, TLR2 and TLR4 in patients with sepsis compared to controls (p < 0.01). In patients with sepsis, death was associated with significant lower CD14 and TLR2 expression at admission (CD14: 25.7 +- 19.1 vs 39.1 +- 17.3 mean fluorescence intensity [MFI], p = 0.02; TLR2: 21.8 +- 9.4 vs. 30.9 +- 9.6, p = 0.01). At 72 hours the TLR2 expression on monocytes was associated with the IL-10 inducibility after LPS stimulation (r = 0.52, p = 0.02) and the CD14 expression with the IL-6, IL-10 and TNF inducibility.We conclude that septic patients are characterized by an increased expression of CD14, TLR2 and TLR4 on monocytes compared to controls. Death is associated with downregulation of TLR2 and CD14 expression on monocytes correlating with reduced cytokine inducibility. We suggest that CD14 and TLR2 are a key factor in monocyte hyporesponsibility during severe sepsis.
Figures
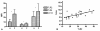
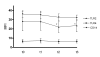
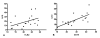
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 on CD14dimCD16+ monocytes in response to sepsis-related antigens.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Aug;141(2):270-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02839.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15996191 Free PMC article.
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (Trem-1) on blood neutrophils is associated with cytokine inducibility in human E. coli sepsis.Diagn Pathol. 2013 Feb 15;8:24. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-24. Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23414215 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and involvement of Toll-like receptors (TLR)2, TLR4, and CD14 in monocyte TNF-alpha production induced by lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis.Med Sci Monit. 2003 Aug;9(8):BR316-24. Med Sci Monit. 2003. PMID: 12942028
-
TLR2, TLR4, CD14, CD11B, and CD11C expressions on monocytes surface and cytokine production in patients with sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock.Shock. 2006 Apr;25(4):351-7. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000217815.57727.29. Shock. 2006. PMID: 16670636
-
Modulation of the lipopolysaccharide receptor complex (CD14, TLR4, MD-2) and toll-like receptor 2 in systemic inflammatory response syndrome-positive patients with and without infection: relationship to tolerance.Shock. 2003 Nov;20(5):415-9. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000092269.01859.44. Shock. 2003. PMID: 14560104
Cited by
-
Effect of zinc supplementation on relative expression of immune response genes in neonates with sepsis: A preliminary study.Indian J Med Res. 2020 Sep;152(3):296-302. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_557_18. Indian J Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33107490 Free PMC article.
-
Early measurement of IL-10 predicts the outcomes of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 21;7(1):1021. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01225-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28432351 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 in experimental Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028619. Epub 2011 Dec 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22163046 Free PMC article.
-
Substance P primes lipoteichoic acid- and Pam3CysSerLys4-mediated activation of human mast cells by up-regulating Toll-like receptor 2.Immunology. 2010 Oct;131(2):220-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03296.x. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20497485 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for Monocyte Reprogramming in a Long-Term Postsepsis Study.Crit Care Explor. 2022 Jul 29;4(8):e0734. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000734. eCollection 2022 Aug. Crit Care Explor. 2022. PMID: 35928539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manthey CL, Vogel SN. Interactions of Lipopolysaccharide With Macrophages. Immunol Ser. 1994;60:63–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

