Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) modulates the toxicity of mixed organophosphorus compounds
- PMID: 19371602
- PMCID: PMC2717945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.02.001
Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) modulates the toxicity of mixed organophosphorus compounds
Abstract
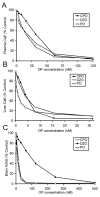
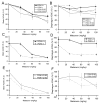
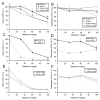
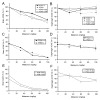
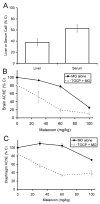
A transgenic mouse model of the human hPON1(Q192R) polymorphism was used to address the role of paraoxonase (PON1) in modulating toxicity associated with exposure to mixtures of organophosphorus (OP) compounds. Chlorpyrifos oxon (CPO), diazoxon (DZO), and paraoxon (PO) are potent inhibitors of carboxylesterases (CaE). We hypothesized that a prior exposure to these OPs would increase sensitivity to malaoxon (MO), a CaE substrate, and the degree of the effect would vary among PON1 genotypes if the OP was a physiologically significant PON1 substrate in vivo. CPO and DZO are detoxified by PON1. For CPO hydrolysis, hPON1(R192) has a higher catalytic efficiency than hPON1(Q192). For DZO hydrolysis, the two alloforms have nearly equal catalytic efficiencies. For PO hydrolysis, the catalytic efficiency of PON1 is too low to be physiologically relevant. When wild-type mice were exposed dermally to CPO, DZO, or PO followed 4-h later by increasing doses of MO, toxicity was increased compared to mice receiving MO alone, presumably due to CaE inhibition. Potentiation of MO toxicity by CPO and DZO was greater in PON1(-/-) mice, which have greatly reduced capacity to detoxify CPO or DZO. Potentiation by CPO was more pronounced in hPON1(Q192) mice than in hPON1(R192) mice due to the decreased efficiency of hPON1(Q192) for detoxifying CPO. Potentiation by DZO was similar in hPON1(Q192) and hPON1(R192) mice, which are equally efficient at hydrolyzing DZO. Potentiation by PO was equivalent among all four genotypes. These results indicate that PON1 status can have a major influence on CaE-mediated detoxication of OP compounds.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The toxicity of mixtures of specific organophosphate compounds is modulated by paraoxonase 1 status.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;660:47-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-350-3_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20221870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) status and substrate hydrolysis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Feb 15;235(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Nov 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19071155 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of chlorpyrifos and chlorpyrifos oxon in a transgenic mouse model of the human paraoxonase (PON1) Q192R polymorphism.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2005 Aug;15(8):589-98. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000167327.08034.d2. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16007003
-
Repeated developmental exposure of mice to chlorpyrifos oxon is associated with paraoxonase 1 (PON1)-modulated effects on cerebellar gene expression.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Sep;123(1):155-69. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr157. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21673326 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variability in the cytochrome P450-paraoxonase 1 (PON1) pathway for detoxication of organophosphorus compounds.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2007;21(4):197-205. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20181. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17936934 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal exposure to organophosphates, paraoxonase 1, and cognitive development in childhood.Environ Health Perspect. 2011 Aug;119(8):1182-8. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1003183. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Environ Health Perspect. 2011. PMID: 21507778 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenetics of paraoxonase activity: elucidating the role of high-density lipoprotein in disease.Pharmacogenomics. 2013 Sep;14(12):1495-515. doi: 10.2217/pgs.13.147. Pharmacogenomics. 2013. PMID: 24024900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Household organophosphorus pesticide use and Parkinson's disease.Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Oct;42(5):1476-85. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt170. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Int J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 24057998 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobehavioral assessment of mice following repeated postnatal exposure to chlorpyrifos-oxon.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012 May-Jun;34(3):311-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012. PMID: 22425525 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and social deficits and enhanced sensitivity to prenatal chlorpyrifos in PON1-/- mouse pups and adults.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 25;15(9):e0239738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239738. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32976529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abernathy CO, Casida JE. Pyrethroid insecticides: esterase cleavage in relation to selective toxicity. Science. 1973;179:1235–1236. - PubMed
-
- Buratti FM, Testai E. Malathion detoxication by human hepatic carboxylesterase and its inhibition by isomalathion and other pesticides. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2005;19(6):406–414. - PubMed
-
- Casida JE, Eto M, Baron RL. Biological activity of a tri-o-cresyl phosphate metabolite. Nature. 1961;191:1396–1397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

