Induction of heme oxygenase 1 by arsenite inhibits cytokine-induced monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells
- PMID: 19371606
- PMCID: PMC3619387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.023
Induction of heme oxygenase 1 by arsenite inhibits cytokine-induced monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells
Abstract
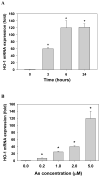
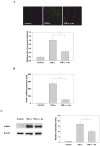
Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is an oxidative stress responsive gene upregulated by various physiological and exogenous stimuli. Arsenite, as an oxidative stressor, is a potent inducer of HO-1 in human and rodent cells. In this study, we investigated the mechanistic role of arsenite-induced HO-1 in modulating tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) induced monocyte adhesion to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Arsenite pretreatment, which upregulated HO-1 in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, inhibited TNF-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion to HUVEC and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 protein expression by 50% and 40%, respectively. Importantly, knockdown of HO-1 by small interfering RNA abolished the arsenite-induced inhibitory effects. These results indicate that induction of HO-1 by arsenite inhibits the cytokine-induced monocyte adhesion to HUVEC by suppressing adhesion molecule expression. These findings established an important mechanistic link between the functional monocyte adhesion properties of HUVEC and the induction of HO-1 by arsenite.
Figures

References
-
- Balakumar P, Kaur T, Singh M. Potential target sites to modulate vascular endothelial dysfunction: Current perspectives and future directions. Toxicology. 2008;245:49–64. - PubMed
-
- Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Waterland RA, Styblo M, Achanzar WE, Webber MM, Waalkes MP. Molecular events associated with arsenic-induced malignant transformation of human prostatic epithelial cells: aberrant genomic DNA methylation and K-ras oncogene activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;206:288–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

