Bile acids inhibit duodenal secretin expression via orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP)
- PMID: 19372104
- PMCID: PMC2711755
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00094.2009
Bile acids inhibit duodenal secretin expression via orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP)
Abstract
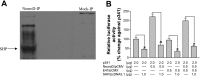
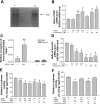
Small heterodimer partner (SHP) is an orphan nuclear receptor in which gene expression can be upregulated by bile acids. It regulates its target genes by repressing the transcriptional activities of other nuclear receptors including NeuroD, which has been shown to regulate secretin gene expression. Here, we evaluated the regulation on duodenal secretin gene expression by SHP and selected bile acids, cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). In vitro treatment of CDCA or fexaramine elevated the SHP transcript level and occupancy on secretin promoter. The increase in the SHP level, induced by bile acid treatment or overexpression, reduced secretin gene expression, whereas this gene inhibitory effect was reversed by silencing of endogenous SHP. In in vivo studies, double-immunofluorescence staining demonstrated the coexpression of secretin and SHP in mouse duodenum. Feeding mice with 1% CA-enriched rodent chow resulted in upregulation of SHP and a concomitant decrease in secretin transcript and protein levels in duodenum compared with the control group fed with normal chow. A diet enriched with 5% cholestyramine led to a decrease in SHP level and a corresponding increase in secretin expression. Overall, this study showed that bile acids via SHP inhibit duodenal secretin gene expression. Because secretin is a key hormone that stimulates bile flow in cholangiocytes, this pathway thus provides a novel means to modulate secretin-stimulated choleresis in response to intraduodenal bile acids.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Localization of small heterodimer partner (SHP) and secretin in mouse duodenal cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Jul;1070:371-5. doi: 10.1196/annals.1317.047. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 16888194
-
Inhibitory effect of the small heterodimer partner on hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 mediates bile acid-induced repression of the human angiotensinogen gene.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):7770-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310577200. Epub 2003 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14672953
-
Low retinol levels differentially modulate bile salt-induced expression of human and mouse hepatic bile salt transporters.Hepatology. 2009 Jan;49(1):151-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.22661. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19111018
-
Structure and function of the atypical orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner.Int Rev Cytol. 2007;261:117-58. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(07)61003-1. Int Rev Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17560281 Review.
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of bile acids on the onset of fructose-induced hepatic steatosis in mice.J Lipid Res. 2010 Dec;51(12):3414-24. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M007179. Epub 2010 Sep 16. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20847296 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of secretin ameliorates biliary and liver phenotypes during alcohol-induced hepatotoxicity.Cell Biosci. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00945-w. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36624475 Free PMC article.
-
The secretin/secretin receptor axis modulates liver fibrosis through changes in transforming growth factor-β1 biliary secretion in mice.Hepatology. 2016 Sep;64(3):865-79. doi: 10.1002/hep.28622. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 27115285 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic adaptation of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli to exposure to bile salts.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 18;9(1):2175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38628-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30778122 Free PMC article.
-
The estrogen-related receptor alpha upregulates secretin expressions in response to hypertonicity and angiotensin II stimulation.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039913. Epub 2012 Jun 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Jiffry BO, Jobling JM, Schloithe AC, Toouli J, Saccone GT. Secretin induces variable inhibition of motility in different parts of the Australian possum sphincter of Oddi. Neurogastroenterol Motil 13: 449–455, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Alpini G, Lenzi R, Zhai WR, Slott PA, Liu MH, Sarkozi L, Tavoloni N. Bile secretory function of intrahepatic biliary epithelium in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 257: G124–G133, 1989. - PubMed
-
- Begley M, Gahan CG, Hill C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29: 625–651, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Ma L, Dawson PA, Sinal CJ, Sehayek E, Gonzalez FJ, Breslow J, Ananthanarayanan M, Shneider BL. Liver receptor homologue-1 mediates species- and cell line-specific bile acid-dependent negative feedback regulation of the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Biol Chem 278: 19909–19916, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

