Endovascular treatment of epistaxis
- PMID: 19372207
- PMCID: PMC7051515
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1607
Endovascular treatment of epistaxis
Abstract
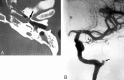
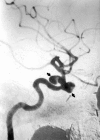
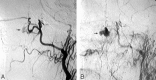
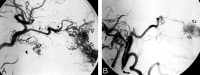
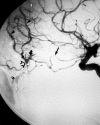
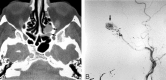
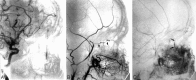
Epistaxis is a common condition that can be managed conservatively in most cases. When these measures, including anterior and posterior packing of the nasal cavity, are unsuccessful at controlling the bleeding, interruption of the blood supply to the sinonasal area can be performed, either by surgical ligation or by transarterial embolization. Embolization should be preceded by thorough diagnostic angiography. Aside from aiding with subsequent selective catheterization and embolization, such angiography may reveal significant anatomic anomalies, anastomoses, or an unsuspected cause of epistaxis. Taking these findings into account, the interventionalist may decide to refrain from embolization or adjust the technique to minimize the risk of adverse events, which are mostly related to inadvertent embolization of the internal carotid artery or ophthalmic artery. We present a review of the various causes of epistaxis and the treatment options, with emphasis on endovascular embolization. We also describe the protocol of our institution for endovascular management of this condition.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Principles of interventional treatment in epistaxis].HNO. 2019 May;67(5):360-365. doi: 10.1007/s00106-019-0643-5. HNO. 2019. PMID: 30888438 Review. German.
-
Embolization for the treatment of posterior epistaxis. An analysis of 31 cases.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993 Aug;119(8):837-41. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1993.01880200037005. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993. PMID: 8343244
-
[Postraumatic massive epistaxis. An indication for selective arterial embolization].An Otorrinolaringol Ibero Am. 2005;32(5):453-8. An Otorrinolaringol Ibero Am. 2005. PMID: 16318088 Spanish.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Nosebleed (Epistaxis).Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(1_suppl):S1-S38. doi: 10.1177/0194599819890327. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31910111
-
Recent trends in epistaxis management in the United States: 2008-2010.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Dec;139(12):1279-84. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2013.5220. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013. PMID: 24136624 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Endoscopic Internal Maxillary Artery Ligation in Intractable Idiopathic Epistaxis.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jun;72(2):228-233. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-01788-y. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32551282 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive understanding of vascular anatomy for endovascular treatment of intractable oronasal bleeding.Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2018 Jun;35(1):7-16. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2018.35.1.7. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2018. PMID: 31620565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence, risk factors, management and prevention of severe postoperative epistaxis after endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: a single center experience.Front Surg. 2023 Jul 26;10:1203409. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1203409. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37564115 Free PMC article.
-
Last resort: case of clot translocation in intra-arterial stroke therapy.BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Jan 6;2014:bcr2013010958. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-010958. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 24395869 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial endovascular treatment in the management of life-threatening intra- and postoperative haemorrhages after otorhinolaryngological surgery.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Jun;269(6):1677-83. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1823-4. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22081095
References
-
- Small M, Murray JA, Maran AG. A study of patients with epistaxis requiring admission to hospital. Health Bull (Edinb) 1982;40:20–29 - PubMed
-
- Pallin DJ, Chng YM, McKay MP, et al. Epidemiology of epistaxis in US emergency departments, 1992 to 2001. Ann Emerg Med 2005;46:77–81 - PubMed
-
- Walker TW, Macfarlane TV, McGarry GW. The epidemiology and chronobiology of epistaxis: an investigation of Scottish hospital admissions 1995–2004. Clin Otolaryngol 2007;32:361–65 - PubMed
-
- Manfredini R, Gallerani M, Portaluppi F. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of epistaxis. Am J Med 2000;108:759–60 - PubMed
-
- Danielides V, Kontogiannis N, Bartzokas A, et al. The influence of meteorological factors on the frequency of epistaxis. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 2002;27:84–88 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
