Metabolite profiling reveals YihU as a novel hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase for alternative succinic semialdehyde metabolism in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 19372223
- PMCID: PMC2713508
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.002089
Metabolite profiling reveals YihU as a novel hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase for alternative succinic semialdehyde metabolism in Escherichia coli
Abstract
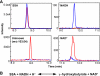
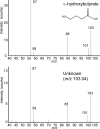
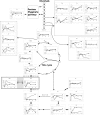
The search for novel enzymes and enzymatic activities is important to map out all metabolic activities and reveal cellular metabolic processes in a more exhaustive manner. Here we present biochemical and physiological evidence for the function of the uncharacterized protein YihU in Escherichia coli using metabolite profiling by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. To detect enzymatic activity and simultaneously identify possible substrates and products of the putative enzyme, we profiled a complex mixture of metabolites in the presence or absence of YihU. In this manner, succinic semialdehyde was identified as a substrate for YihU. The purified YihU protein catalyzed in vitro the NADH-dependent reduction of succinic semialdehyde to gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Moreover, a yihU deletion mutant displayed reduced tolerance to the cytotoxic effects of exogenous addition of succinic semialdehyde. Profiling of intracellular metabolites following treatment of E. coli with succinic semialdehyde supports the existence of a YihU-catalyzed reduction of succinic semialdehyde to gamma-hydroxybutyrate in addition to its known oxidation to succinate and through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. These findings suggest that YihU is a novel gamma-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase involved in the metabolism of succinic semialdehyde, and other potentially toxic intermediates that may accumulate under stress conditions in E. coli.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Succinic semialdehyde reductase Gox1801 from Gluconobacter oxydans in comparison to other succinic semialdehyde-reducing enzymes.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 May;99(9):3929-39. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6191-8. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25425279
-
A novel gamma-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase: identification and expression of an Arabidopsis cDNA and potential role under oxygen deficiency.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41552-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305717200. Epub 2003 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12882961
-
Mutants of GABA transaminase (POP2) suppress the severe phenotype of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ssadh) mutants in Arabidopsis.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003383. Epub 2008 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18846220 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of aldehyde dehydrogenase 5a1 (succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase) and accumulation of gamma-hydroxybutyrate associated with its deficiency.Hum Genomics. 2009 Jan;3(2):106-20. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-3-2-106. Hum Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19164088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, and neurological disease.Ann Neurol. 2003;54 Suppl 6:S3-12. doi: 10.1002/ana.10696. Ann Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12891648 Review.
Cited by
-
Nontargeted in vitro metabolomics for high-throughput identification of novel enzymes in Escherichia coli.Nat Methods. 2017 Feb;14(2):187-194. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4103. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Nat Methods. 2017. PMID: 27941785
-
Closing the loop on the GABA shunt in plants: are GABA metabolism and signaling entwined?Front Plant Sci. 2015 Jun 9;6:419. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00419. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26106401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intensive DNA Replication and Metabolism during the Lag Phase in Cyanobacteria.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 2;10(9):e0136800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136800. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26331851 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic strategies for the identification of new enzyme functions and metabolic pathways.EMBO Rep. 2014 Jun;15(6):657-69. doi: 10.15252/embr.201338283. Epub 2014 May 14. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24829223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical and structural studies of uncharacterized protein PA0743 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa revealed NAD+-dependent L-serine dehydrogenase.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 13;287(3):1874-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.294561. Epub 2011 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22128181 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

