ERK signaling in the pituitary is required for female but not male fertility
- PMID: 19372235
- PMCID: PMC2703601
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0030
ERK signaling in the pituitary is required for female but not male fertility
Abstract
Males and females require different patterns of pituitary gonadotropin secretion for fertility. The mechanisms underlying these gender-specific profiles of pituitary hormone production are unknown; however, they are fundamental to understanding the sexually dimorphic control of reproductive function at the molecular level. Several studies suggest that ERK1 and -2 are essential modulators of hypothalamic GnRH-mediated regulation of pituitary gonadotropin production and fertility. To test this hypothesis, we generated mice with a pituitary-specific depletion of ERK1 and 2 and examined a range of physiological parameters including fertility. We find that ERK signaling is required in females for ovulation and fertility, whereas male reproductive function is unaffected by this signaling deficiency. The effects of ERK pathway ablation on LH biosynthesis underlie this gender-specific phenotype, and the molecular mechanism involves a requirement for ERK-dependent up-regulation of the transcription factor Egr1, which is necessary for LHbeta expression. Together, these findings represent a significant advance in elucidating the molecular basis of gender-specific regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and sexually dimorphic control of fertility.
Figures
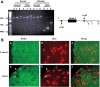
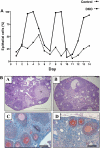

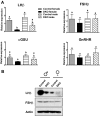
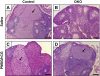
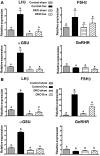
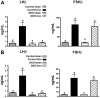
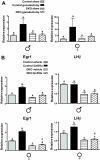
References
-
- Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH 2001 Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183 - PubMed
-
- Mazzucchelli C, Vantaggiato C, Ciamei A, Fasano S, Pakhotin P, Krezel W, Welzl H, Wolfer DP, Pagès G, Valverde O, Marowsky A, Porrazzo A, Orban PC, Maldonado R, Ehrengruber MU, Cestari V, Lipp HP, Chapman PF, Pouysségur J, Brambilla R 2002 Knockout of ERK1 MAP kinase enhances synaptic plasticity in the striatum and facilitates striatal-mediated learning and memory. Neuron 34:807–820 - PubMed
-
- Nekrasova T, Shive C, Gao Y, Kawamura K, Guardia R, Landreth G, Forsthuber TG 2005 ERK1-deficient mice show normal T cell effector function and are highly susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 175:2374–2380 - PubMed
-
- Newbern J, Zhong J, Wickramasinghe SR, Li X, Wu Y, Samuels I, Cherosky N, Karlo JC, O'Loughlin B, Wikenheiser J, Gargesha M, Doughman YQ, Charron J, Ginty DD, Watanabe M, Saitta SC, Snider WD, Landreth GE 2008 Mouse and human phenotypes indicate a critical conserved role for ERK2 signaling in neural crest development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:17115–17120 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

