The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain
- PMID: 19372393
- PMCID: PMC3263819
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1169786
The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain
Abstract
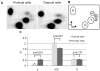
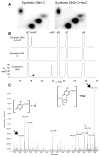
Despite the importance of epigenetic regulation in neurological disorders, little is known about neuronal chromatin. Cerebellar Purkinje neurons have large and euchromatic nuclei, whereas granule cell nuclei are small and have a more typical heterochromatin distribution. While comparing the abundance of 5-methylcytosine in Purkinje and granule cell nuclei, we detected the presence of an unusual DNA nucleotide. Using thin-layer chromatography, high-pressure liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry, we identified the nucleotide as 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxycytidine (hmdC). hmdC constitutes 0.6% of total nucleotides in Purkinje cells, 0.2% in granule cells, and is not present in cancer cell lines. hmdC is a constituent of nuclear DNA that is highly abundant in the brain, suggesting a role in epigenetic control of neuronal function.
Figures
Comment in
-
5-hydroxymethylcytosine, a modified mammalian DNA base with a potential regulatory role.Epigenomics. 2009 Oct;1(1):21-2. doi: 10.2217/epi.09.18. Epigenomics. 2009. PMID: 22122633 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

