Increased AKT S473 phosphorylation after mTORC1 inhibition is rictor dependent and does not predict tumor cell response to PI3K/mTOR inhibition
- PMID: 19372546
- PMCID: PMC3440776
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0668
Increased AKT S473 phosphorylation after mTORC1 inhibition is rictor dependent and does not predict tumor cell response to PI3K/mTOR inhibition
Abstract
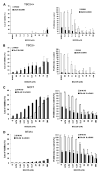
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) regulates cellular processes important for progression of human cancer. RAD001 (everolimus), an mTORC1 (mTOR/raptor) inhibitor, has broad antitumor activity in preclinical models and cancer patients. Although most tumor lines are RAD001 sensitive, some are not. Selective mTORC1 inhibition can elicit increased AKT S473 phosphorylation, involving insulin receptor substrate 1, which is suggested to potentially attenuate effects on tumor cell proliferation and viability. Rictor may also play a role because rictor kinase complexes (including mTOR/rictor) regulate AKT S473 phosphorylation. The role of raptor and rictor in the in vitro response of human cancer cells to RAD001 was investigated. Using a large panel of cell lines representing different tumor histotypes, the basal phosphorylation of AKT S473 and some AKT substrates was found to correlate with the antiproliferative response to RAD001. In contrast, increased AKT S473 phosphorylation induced by RAD001 did not correlate. Similar increases in AKT phosphorylation occurred following raptor depletion using siRNA. Strikingly, rictor down-regulation attenuated AKT S473 phosphorylation induced by mTORC1 inhibition. Further analyses showed no relationship between modulation of AKT phosphorylation on S473 and T308 and AKT substrate phosphorylation patterns. Using a dual pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mTOR catalytic inhibitor (NVP-BEZ235), currently in phase I trials, concomitant targeting of these kinases inhibited AKT S473 phosphorylation, eliciting more profound cellular responses than mTORC1 inhibition alone. However, reduced cell viability could not be predicted from biochemical or cellular responses to mTORC1 inhibitors. These data could have implications for the clinical application of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mTOR inhibitors.
Figures



References
-
- Bhaskar PT, Hay N. The two TORCs and Akt. Dev Cell. 2007;12:487–502. - PubMed
-
- Boulay A, Lane HA. The mammalian target of rapamycin kinase and tumor growth inhibition. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007;172:99–124. - PubMed
-
- Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Chiang GC, Abraham RT. Targeting the mTOR signaling network in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:433–42. - PubMed
-
- Beuvink I, Boulay A, Fumagalli S, et al. The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes tumor cells to DNA-damaged induced apoptosis through inhibition of p21 translation. Cell. 2005;120:747–59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

