Molecular discrimination of structurally equivalent Lys 63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains
- PMID: 19373254
- PMCID: PMC2680876
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.55
Molecular discrimination of structurally equivalent Lys 63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains
Abstract
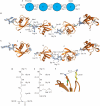
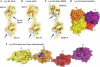
At least eight types of ubiquitin chain exist, and individual linkages affect distinct cellular processes. The only distinguishing feature of differently linked ubiquitin chains is their structure, as polymers of the same unit are chemically identical. Here, we have crystallized Lys 63-linked and linear ubiquitin dimers, revealing that both adopt equivalent open conformations, forming no contacts between ubiquitin molecules and thereby differing significantly from Lys 48-linked ubiquitin chains. We also examined the specificity of various deubiquitinases (DUBs) and ubiquitin-binding domains (UBDs). All analysed DUBs, except CYLD, cleave linear chains less efficiently compared with other chain types, or not at all. Likewise, UBDs can show chain specificity, and are able to select distinct linkages from a ubiquitin chain mixture. We found that the UBAN (ubiquitin binding in ABIN and NEMO) motif of NEMO (NF-kappaB essential modifier) binds to linear chains exclusively, whereas the NZF (Npl4 zinc finger) domain of TAB2 (TAK1 binding protein 2) is Lys 63 specific. Our results highlight remarkable specificity determinants within the ubiquitin system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adhikari A, Xu M, Chen ZJ (2007) Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene 26: 3214–3226 - PubMed
-
- Clague MJ, Urbe S (2006) Endocytosis: the DUB version. Trends Cell Biol 16: 551–559 - PubMed
-
- Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFα requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 22: 245–257 - PubMed
-
- Eddins MJ, Varadan R, Fushman D, Pickart CM, Wolberger C (2007) Crystal structure and solution NMR studies of Lys 48-linked tetraubiquitin at neutral pH. J Mol Biol 367: 204–211 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

