Bile acids conjugation in human bile is not random: new insights from (1)H-NMR spectroscopy at 800 MHz
- PMID: 19373503
- PMCID: PMC5459358
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-009-3296-4
Bile acids conjugation in human bile is not random: new insights from (1)H-NMR spectroscopy at 800 MHz
Abstract
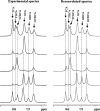
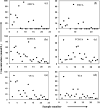
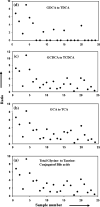
Bile acids constitute a group of structurally closely related molecules and represent the most abundant constituents of human bile. Investigations of bile acids have garnered increased interest owing to their recently discovered additional biological functions including their role as signaling molecules that govern glucose, fat and energy metabolism. Recent NMR methodological developments have enabled single-step analysis of several highly abundant and common glycine- and taurine- conjugated bile acids, such as glycocholic acid, glycodeoxycholic acid, glycochenodeoxycholic acid, taurocholic acid, taurodeoxycholic acid, and taurochenodeoxycholic acid. Investigation of these conjugated bile acids in human bile employing high field (800 MHz) (1)H-NMR spectroscopy reveals that the ratios between two glycine-conjugated bile acids and their taurine counterparts correlate positively (R2 = 0.83-0.97; p = 0.001 x 10(-2)-0.006 x 10(-7)) as do the ratios between a glycine-conjugated bile acid and its taurine counterpart (R2 = 0.92-0.95; p = 0.004 x 10(-3)-0.002 x 10(-10)). Using such correlations, concentration of individual bile acids in each sample could be predicted in good agreement with the experimentally determined values. These insights into the pattern of bile acid conjugation in human bile between glycine and taurine promise useful clues to the mechanism of bile acids' biosynthesis, conjugation and enterohepatic circulation, and may improve our understanding of the role of individual conjugated bile acids in health and disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
1H and 13C NMR characterization and stereochemical assignments of bile acids in aqueous media.Lipids. 2005 Oct;40(10):1031-41. doi: 10.1007/s11745-005-1466-1. Lipids. 2005. PMID: 16382575
-
Identification of metabolites in human hepatic bile using 800 MHz 1H NMR spectroscopy, HPLC-NMR/MS and UPLC-MS.Mol Biosyst. 2009 Feb;5(2):180-90. doi: 10.1039/b814426e. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Mol Biosyst. 2009. PMID: 19156264
-
Single-step analysis of individual conjugated bile acids in human bile using 1H NMR spectroscopy.Lipids. 2006 Jun;41(6):591-603. doi: 10.1007/s11745-006-5008-7. Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16981437
-
Quantification of glycine and taurine conjugated bile acids in human bile using 1H NMR spectroscopy.Magn Reson Med. 2005 Jun;53(6):1441-6. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20513. Magn Reson Med. 2005. PMID: 15906301
-
Bile acid solubility and precipitation in vitro and in vivo: the role of conjugation, pH, and Ca2+ ions.J Lipid Res. 1992 May;33(5):617-26. J Lipid Res. 1992. PMID: 1619357 Review.
Cited by
-
Bile salt hydrolases shape the bile acid landscape and restrict Clostridioides difficile growth in the murine gut.Nat Microbiol. 2023 Apr;8(4):611-628. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01337-7. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36914755 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Oncology via NMR-Based Metabolomics: A Review on Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4687. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094687. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot Multi-Omic Analysis of Human Bile from Benign and Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Machine-Learning Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 21;12(6):1644. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061644. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575903 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Taurocholate Stimulates Campylobacter jejuni Outer Membrane Vesicle Production via Down-Regulation of the Maintenance of Lipid Asymmetry Pathway.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 29;9:177. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00177. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31192166 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in NMR-based biofluid analysis and metabolite profiling.Analyst. 2010 Jul;135(7):1490-8. doi: 10.1039/c000091d. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Analyst. 2010. PMID: 20379603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang W, Ma K, Zhang J, Qatanani M, Cuvillier J, Liu J, Dong B, Huang X, Moore DD. Nuclear receptor-dependent bile acid signaling is required for normal liver regeneration. Science. 2006;312(5771):233–236. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Houten SM, Mataki C, Christoffolete MA, Kim BW, Sato H, Messaddeq N, Harney JW, Ezaki O, Kodama T, Schoonjans K, Bianco AC, Auwerx J. Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature. 2006;439(7075):484–489. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann AF. The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159(22):2647–2658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

