Effects of selenite and genistein on G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 19373614
- PMCID: PMC2724066
- DOI: 10.1080/01635580802582751
Effects of selenite and genistein on G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
Abstract
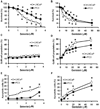
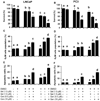
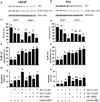
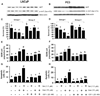
Combination of chemopreventive agents with distinct molecular mechanisms is considered to offer a potential for enhancing cancer prevention efficacy while minimizing toxicity. Here we report two chemopreventive agents, selenite and genistein, that have synergistic effects on apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and associated signaling pathways in p53-expressing LNCaP and p53-null PC3 prostate cancer cells. We show that selenite induced apoptosis only, whereas genistein induced both apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. Combination of these two agents exhibited enhanced effects, which were slightly greater in LNCaP than PC3 cells. Selenite or genistein alone upregulated protein levels of p53 in LNCaP cells only and p21(waf1) and Bax in both cell lines. Additionally, genistein inhibited AKT phosphorylation. Downregulation of AKT by siRNA caused apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest and masked the effects of genistein. Treatment with insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) elevated levels of total and phosphorylated AKT and suppressed the effects of genistein. Neither downregulation of AKT nor IGF-I treatment altered the cellular effects of selenite. Our study demonstrates that selenium and genistein act via different molecular mechanisms and exhibit enhanced anticancer effects, suggesting that a combination of selenium and genistein may offer better efficacy and reduction of toxicity in prostate cancer prevention.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p53-independent induction of p21 (WAF1/CIP1), reduction of cyclin B1 and G2/M arrest by the isoflavone genistein in human prostate carcinoma cells.Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000 Feb;91(2):164-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00928.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10761703 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein inhibits radiation-induced activation of NF-kappaB in prostate cancer cells promoting apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest.BMC Cancer. 2006 Apr 26;6:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-107. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16640785 Free PMC article.
-
A concentrated aglycone isoflavone preparation (GCP) that demonstrates potent anti-prostate cancer activity in vitro and in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;10(15):5282-92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0828. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15297432
-
Expression of p53 enhances selenite-induced superoxide production and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;66(4):2296-304. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2216. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16489034 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct effects of methylseleninic acid versus selenite on apoptosis, cell cycle, and protein kinase pathways in DU145 human prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2002 Oct;1(12):1059-66. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002. PMID: 12481429
Cited by
-
Novel library of selenocompounds as kinase modulators.Molecules. 2011 Jul 27;16(8):6349-64. doi: 10.3390/molecules16086349. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21796074 Free PMC article.
-
The solvent and treatment regimen of sodium selenite cause its effects to vary on the radiation response of human bronchial cells from tumour and normal tissues.Med Oncol. 2020 Nov 18;37(12):115. doi: 10.1007/s12032-020-01437-y. Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33205219 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs 221/222 and genistein-mediated regulation of ARHI tumor suppressor gene in prostate cancer.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011 Jan;4(1):76-86. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0167. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011. PMID: 21071579 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphanegold(I) thiolates, Ph3PAu[SC(OR)=NC 6H 4Me-4] for R = Me, Et and iPr, induce apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and inhibit cell invasion of HT-29 colon cancer cells through modulation of the nuclear factor-κB activation pathway and ubiquitination.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015 Jul;20(5):855-73. doi: 10.1007/s00775-015-1271-5. Epub 2015 May 24. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015. PMID: 26003312
-
Apoptotic effects of genistein, biochanin-A and apigenin on LNCaP and PC-3 cells by p21 through transcriptional inhibition of polo-like kinase-1.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Nov;26(11):1489-94. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.11.1489. Epub 2011 Oct 27. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22065906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albano JD, Ward E, Jemal A, Anderson R, Cokkinides VE, et al. Cancer mortality in the United States by education level and race. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1384–1394. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M, Colombet M, et al. Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:581–592. - PubMed
-
- Combs GF, Jr, Gray WP. Chemopreventive agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther. 1998;79:179–192. - PubMed
-
- Schrauzer GN, White DA, Schneider CJ. Cancer mortality correlation studies—III: statistical associations with dietary selenium intakes. Bioinorg Chem. 1977;7:23–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
