Nanometer distance measurements between multicolor quantum dots
- PMID: 19374434
- PMCID: PMC2748936
- DOI: 10.1021/nl901163k
Nanometer distance measurements between multicolor quantum dots
Abstract
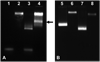
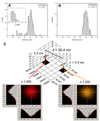
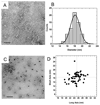
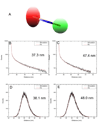
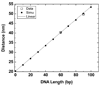
Quantum dot dimers made of short double-stranded DNA molecules labeled with different color quantum dots at each end were imaged using multicolor stage-scanning confocal microscopy. This approach eliminates chromatic aberration and color registration issues usually encountered in other multicolor imaging techniques. We demonstrate nanometer accuracy in individual distance measurement by suppression of quantum dot blinking and thoroughly characterize the contribution of different effects to the variability observed between measurements. Our analysis opens the way to accurate structural studies of biomolecules and biomolecular complexes using multicolor quantum labeling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of single DNA molecules by multicolor quantum-dot end-labeling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jun 20;33(11):e98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni097. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15967805 Free PMC article.
-
Single-step multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization using semiconductor quantum dot-DNA conjugates.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006;45(1):59-70. doi: 10.1385/CBB:45:1:59. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006. PMID: 16679564 Free PMC article.
-
Superlocalization spectral imaging microscopy of a multicolor quantum dot complex.Anal Chem. 2012 Feb 7;84(3):1504-9. doi: 10.1021/ac202784h. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22304482
-
Quantum Dot-Based Simultaneous Multicolor Imaging.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Aug;22(4):820-831. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01432-4. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 31529409 Review.
-
Quantum dot: magic nanoparticle for imaging, detection and targeting.Acta Biomed. 2009 Aug;80(2):156-65. Acta Biomed. 2009. PMID: 19848055 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging nanometre-scale structure in cells using in situ aberration correction.J Microsc. 2012 Oct;248(1):90-101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2012.03654.x. Epub 2012 Aug 20. J Microsc. 2012. PMID: 22906048 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Toxicity of Quantum Dots through Biliometric Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 27;18(11):5768. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115768. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34072155 Free PMC article.
-
Subnanometre single-molecule localization, registration and distance measurements.Nature. 2010 Jul 29;466(7306):647-51. doi: 10.1038/nature09163. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20613725
-
Probing the "dark" fraction of core-shell quantum dots by ensemble and single particle pH-dependent spectroscopy.ACS Nano. 2011 Nov 22;5(11):9062-73. doi: 10.1021/nn203272p. Epub 2011 Oct 28. ACS Nano. 2011. PMID: 22023370 Free PMC article.
-
Direct optical mapping of transcription factor binding sites on field-stretched λ-DNA in nanofluidic devices.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):e85. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku254. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24753422 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

