No consistent difference in gray matter volume between individuals with fibromyalgia and age-matched healthy subjects when controlling for affective disorder
- PMID: 19375224
- PMCID: PMC2719961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.03.017
No consistent difference in gray matter volume between individuals with fibromyalgia and age-matched healthy subjects when controlling for affective disorder
Abstract
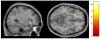
Fibromyalgia (FM) is thought to involve abnormalities in central pain processing. Recent studies involving small samples have suggested alterations in gray matter volume (GMV) in brains of FM patients. Our objective was to verify these findings in a somewhat larger sample using voxel-based morphometry (VBM), while controlling for the presence of affective disorders (AD). T1-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) brain scans were obtained on 29 FM patients with AD, 29 FM patients without AD, and 29 age-matched healthy controls (HCs) using a 3T scanner. Segmentation, spatial normalization, and volumetric modulation were performed using an automated protocol within SPM5. Smoothed gray matter segments were entered into a voxel-wise one-way ANOVA, and a search for significant clusters was performed using thresholding methods published in previous studies (whole-brain threshold of p<.05 correcting for multiple comparisons; region-of-interest (ROI) threshold of p< or =.001 uncorrected, or p<.05 small-volume corrected). The whole-brain analysis did not reveal any significant clusters. ROI-based analysis revealed a significant difference in left anterior insula GMV among the three groups (xyz={-28, 21, 9}; p=.026, corrected). However, on post-hoc testing, FM patients without AD did not differ significantly from HC with respect to mean GMV extracted from this cluster. A significant negative correlation was found between mean cluster GMV and scores of trait anxiety (State-Trait Personality Inventory, Trait Anxiety scale; rho=-.470, p<.001). No other significant clusters were found on ROI-based analysis. Our results emphasize the importance of correcting for AD when carrying out VBM studies in chronic pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alterations of the resting-state brain network connectivity and gray matter volume in patients with fibromyalgia in comparison to ankylosing spondylitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 2;14(1):29960. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79246-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39622846 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel-based morphometric analysis of gray matter in first episode schizophrenia.Neuroimage. 2002 Dec;17(4):1711-9. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1296. Neuroimage. 2002. PMID: 12498745 Free PMC article.
-
Correlating anterior insula gray matter volume changes in young people with clinical and neurocognitive outcomes: an MRI study.BMC Psychiatry. 2012 May 20;12:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-45. BMC Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22607202 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Volumetric Correlates of Apathy in Alzheimer's Disease and Cognitively Normal Older Adults: Meta-Analysis, Label-Based Review, and Study of an Independent Cohort.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(3):1251-1265. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215316. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 34924392 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths With Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;73(1):64-72. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2423. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26650724 Review.
Cited by
-
Psychological characteristics associated with the brain volume of patients with fibromyalgia.Biopsychosoc Med. 2023 Oct 24;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13030-023-00293-2. Biopsychosoc Med. 2023. PMID: 37875931 Free PMC article.
-
Effective treatment of chronic low back pain in humans reverses abnormal brain anatomy and function.J Neurosci. 2011 May 18;31(20):7540-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5280-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21593339 Free PMC article.
-
Can neuroimaging help us to understand and classify somatoform disorders? A systematic and critical review.Psychosom Med. 2011 Feb-Mar;73(2):173-84. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31820824f6. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Psychosom Med. 2011. PMID: 21217095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using structural and functional MRI as a neuroimaging technique to investigate chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalopathy: a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2020 Aug 30;10(8):e031672. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031672. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32868345 Free PMC article.
-
Different pain, different brain: thalamic anatomy in neuropathic and non-neuropathic chronic pain syndromes.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 20;31(16):5956-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5980-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21508220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. Neuroimage. 2000;11:805–21. - PubMed
-
- Barlow JH, Wright CC. Dimensions of the Center of Epidemiological Studies-Depression Scale for people with arthritis from the UK. Psychol Rep. 1998;83:915–9. - PubMed
-
- Bergman S, Herrstrom P, Jacobsson LT, Petersson IF. Chronic widespread pain: a three year followup of pain distribution and risk factors. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:818–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

