Cytokine signaling mediates UV-induced nociceptive sensitization in Drosophila larvae
- PMID: 19375319
- PMCID: PMC4017352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.062
Cytokine signaling mediates UV-induced nociceptive sensitization in Drosophila larvae
Abstract
Background: Heightened nociceptive (pain) sensitivity is an adaptive response to tissue damage and serves to protect the site of injury. Multiple mediators of nociceptive sensitization have been identified in vertebrates, but the complexity of the vertebrate nervous system and tissue-repair responses has hindered identification of the precise roles of these factors.
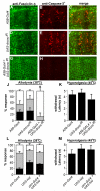
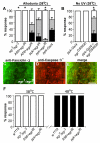
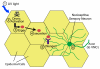
Results: Here we establish a new model of nociceptive sensitization in Drosophila larvae, in which UV-induced tissue damage alters an aversive withdrawal behavior. We find that UV-treated larvae develop both thermal hyperalgesia, manifested as an exaggerated response to noxious thermal stimuli, and thermal allodynia, a responsiveness to subthreshold thermal stimuli that are not normally perceived as noxious. Allodynia is dependent upon a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) homolog, Eiger, released from apoptotic epidermal cells, and the TNF receptor, Wengen, expressed on nociceptive sensory neurons.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that cytokine-mediated nociceptive sensitization is conserved across animal phyla and set the stage for a sophisticated genetic dissection of the cellular and molecular alterations responsible for development of nociceptive sensitization in sensory neurons.
Figures



References
-
- Woolf CJ, Ma Q. Nociceptors--noxious stimulus detectors. Neuron. 2007;55:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Hucho T, Levine JD. Signaling pathways in sensitization: toward a nociceptor cell biology. Neuron. 2007;55:365–376. - PubMed
-
- Ji RR, Woolf CJ. Neuronal plasticity and signal transduction in nociceptive neurons: implications for the initiation and maintenance of pathological pain. Neurobiol Dis. 2001;8:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Dray A. Inflammatory mediators of pain. Br J Anaesth. 1995;75:125–131. - PubMed
-
- Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature. 2001;413:203–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

