The calcium/NFAT pathway: role in development and function of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 19375514
- PMCID: PMC2696553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.04.008
The calcium/NFAT pathway: role in development and function of regulatory T cells
Abstract
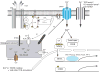
Calcium signals are essential for diverse cellular functions in the immune system. Sustained Ca(2+) entry is necessary for complete and long-lasting activation of calcineurin/NFAT pathways. A growing number of studies have emphasized that Ca(2+)/calcineurin/NFAT pathway is crucial for both development and function of regulatory T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Calcium-Calcineurin-NFAT Signaling Pathway in Health and Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 10;11:195. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00195. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32210952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+-Calcineurin Axis-Controlled NFAT Nuclear Translocation Is Crucial for Optimal T Cell Immunity in an Early Vertebrate.J Immunol. 2020 Feb 1;204(3):569-585. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901065. Epub 2019 Dec 23. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31871019
-
The role of Ca2+ /Calcineurin/NFAT signalling pathway in osteoblastogenesis.Cell Prolif. 2021 Nov;54(11):e13122. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13122. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 34523757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKC-dependent coupling of calcium permeation through transient receptor potential canonical 3 (TRPC3) to calcineurin signaling in HL-1 myocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 28;108(26):10556-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106183108. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21653882 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium and calcineurin-NFAT signaling regulate granulocyte-monocyte progenitor cell cycle via Flt3-L.Stem Cells. 2014 Dec;32(12):3232-44. doi: 10.1002/stem.1813. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 25100642 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Short Overview of Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in Response to Physical Activity and Antioxidant Supplementation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Sep 18;9(9):886. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090886. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32962110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between membrane topology and mechanical forces in regulating T cell receptor activity.Commun Biol. 2022 Jan 11;5(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02995-1. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35017678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of MicroRNAs in Atrial Fibrillation.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Mar 12;2020:3053520. doi: 10.1155/2020/3053520. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32256190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFATC3-PLA2G15 Fusion Transcript Identified by RNA Sequencing Promotes Tumor Invasion and Proliferation in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines.Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan;51(1):391-401. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.103. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 29909608 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic acid inhibits NFAT and IL-2 signaling pathways in regulatory T cells and diminishes their suppressive function in patients with metastatic cancer.Oncoimmunology. 2017 Jun 14;6(8):e1338238. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1338238. eCollection 2017. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 28920001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis RS. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:497–521. - PubMed
-
- Feske S. Calcium signalling in lymphocyte activation and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:690–702. - PubMed
-
- Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003;17:2205–2232. - PubMed
-
- Lewis RS. The molecular choreography of a store-operated calcium channel. Nature. 2007;446:284–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

