Neurorestorative therapies for stroke: underlying mechanisms and translation to the clinic
- PMID: 19375666
- PMCID: PMC2727708
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70061-4
Neurorestorative therapies for stroke: underlying mechanisms and translation to the clinic
Abstract
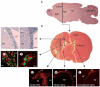
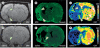
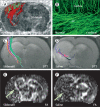
Restorative cell-based and pharmacological therapies for experimental stroke substantially improve functional outcome. These therapies target several types of parenchymal cells (including neural stem cells, cerebral endothelial cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons), leading to enhancement of endogenous neurogenesis, angiogenesis, axonal sprouting, and synaptogenesis in the ischaemic brain. Interaction between these restorative events probably underpins the improvement in functional outcome. This Review provides examples of cell-based and pharmacological restorative treatments for stroke that stimulate brain plasticity and functional recovery. The molecular pathways activated by these therapies, which induce remodelling of the injured brain via angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and axonal and dendritic plasticity, are discussed. The ease of treating intact brain tissue to stimulate functional benefit in restorative therapy compared with treating injured brain tissue in neuroprotective therapy might more readily help with translation of restorative therapy from the laboratory to the clinic.
Figures

References
-
- NINDS Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–87. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1317–29. - PubMed
-
- Kawamata T, Speliotes EK, Finklestein SP. The role of polypeptide growth factors in recovery from stroke. In: Freund H-J, Sabel BA, Witte OW, editors. Brain Plasticity. Lippincott-Raven; Philadephia: 1997. pp. 377–82. - PubMed
-
- Cramer SC, Chopp M. Recovery recapitulates ontogeny. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:265–71. - PubMed
-
- Zhang R, Wang L, Zhang L, et al. Nitric oxide enhances angiogenesis via the synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor and cGMP after stroke in the rat. Circ Res. 2003;92:308–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

