Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks
- PMID: 19376066
- PMCID: PMC2691647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.024
Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks
Abstract
During development, the healthy human brain constructs a host of large-scale, distributed, function-critical neural networks. Neurodegenerative diseases have been thought to target these systems, but this hypothesis has not been systematically tested in living humans. We used network-sensitive neuroimaging methods to show that five different neurodegenerative syndromes cause circumscribed atrophy within five distinct, healthy, human intrinsic functional connectivity networks. We further discovered a direct link between intrinsic connectivity and gray matter structure. Across healthy individuals, nodes within each functional network exhibited tightly correlated gray matter volumes. The findings suggest that human neural networks can be defined by synchronous baseline activity, a unified corticotrophic fate, and selective vulnerability to neurodegenerative illness. Future studies may clarify how these complex systems are assembled during development and undermined by disease.
Figures

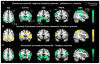
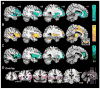
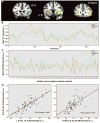
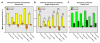
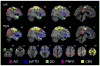
Comment in
-
Defining neurocognitive networks in the BOLD new world of computed connectivity.Neuron. 2009 Apr 16;62(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.04.001. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19376059
References
-
- Bi G, Poo M. Distributed synaptic modification in neural networks induced by patterned stimulation. Nature. 1999;401:792–796. - PubMed
-
- Boccardi M, Sabattoli F, Laakso MP, Testa C, Rossi R, Beltramello A, Soininen H, Frisoni GB. Frontotemporal dementia as a neural system disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Boxer AL, Geschwind MD, Belfor N, Gorno-Tempini ML, Schauer GF, Miller BL, Weiner MW, Rosen HJ. Patterns of brain atrophy that differentiate corticobasal degeneration syndrome from progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:81–86. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

