Protein 4.1R links E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to the cytoskeleton through its direct interaction with beta-catenin and modulates adherens junction integrity
- PMID: 19376086
- PMCID: PMC4409867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.03.022
Protein 4.1R links E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to the cytoskeleton through its direct interaction with beta-catenin and modulates adherens junction integrity
Abstract
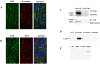
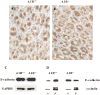
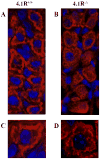
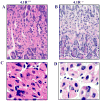
Protein 4.1R (4.1R) is the prototypical member of the protein 4.1 superfamily comprising of the protein 4.1 family (4.1R, 4.1B, 4.1G and 4.1N) and ERM family (ezrin, radixin and meosin). These proteins in general serve as adaptors between the membrane and the cytoskeleton. Here we show that 4.1R expressed in the gastric epithelial cells associates with adherens junction protein beta-catenin. Biochemical examination of 4.1R-deficient stomach epithelia revealed a selective reduction of beta-catenin which is accompanied by a weaker linkage of E-cadherin to the cytoskeleton. In addition, organization of actin cytoskeleton was altered in 4.1R-deficient cells. Moreover, histological examination revealed that cell-cell contacts are impaired and gastric glands are disorganized in 4.1R null stomach epithelia. These results demonstrate an important and previously unidentified role of 4.1R in linking the cadherin/catenin complex to the cytoskeleton through its direct interaction with beta-catenin and in regulating the integrity of adherens junction.
Figures


References
-
- Parra M, Gascard P, Walensky LD, Gimm JA, Blackshaw S, Chan N, Takakuwa Y, Berger T, Lee G, Chasis JA, Snyder SH, Mohandas N, Conboy JG. Molecular and functional characterization of protein 4.1B, a novel member of the protein 4.1 family with high level, focal expression in brain. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:3247–55. - PubMed
-
- Parra M, Gascard P, Walensky LD, Snyder SH, Mohandas N, Conboy JG. Cloning and characterization of 4.1G (EPB41L2), a new member of the skeletal protein 4.1 (EPB41) gene family. Genomics. 1998;49:298–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

