Effect of recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease on serum anti-pneumolysin IgG titres in HIV infected adults
- PMID: 19376181
- PMCID: PMC2791880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.04.026
Effect of recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease on serum anti-pneumolysin IgG titres in HIV infected adults
Abstract
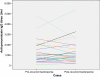
We measured serum anti-pneumolysin IgG concentrations in a prospective cohort of 34 HIV infected adults who developed recurrent pneumococcal bacteraemia, and compared baseline levels with HIV positive and HIV negative control subjects that remained free of pneumococcal disease. Anti-pneumolysin concentrations in HIV positive cases and controls were higher compared to HIV negative controls. There was no significant difference in levels between HIV positive subjects who did and did not subsequently develop pneumococcal bacteraemia (geometric means 849.1 U/ml vs. 564.6 U/ml, p=0.059). Anti-pneumolysin IgG titres before, and after the recurrent episode of pneumococcal bacteraemia did not differ significantly (p=0.95). High levels of anti-pneumolysin IgG do not predict protection from invasive pneumococcal disease or indicate that an effective immune response has occurred in HIV infected patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased IgG but normal IgA anti-pneumococcal protein antibodies in lung of HIV-infected adults.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 2;31(35):3469-72. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.062. Epub 2013 May 10. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23664995 Free PMC article.
-
Otitis-Prone Children Produce Functional Antibodies to Pneumolysin and Pneumococcal Polysaccharides.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017 Mar 6;24(3):e00497-16. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00497-16. Print 2017 Mar. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28031178 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response to pneumolysin and to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide in healthy individuals and Streptococcus pneumoniae infected patients.Vaccine. 2004 Mar 12;22(9-10):1157-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.09.025. Vaccine. 2004. PMID: 15003643 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of serum antibodies to pneumolysin with those to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides in children with acute otitis media.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996 Feb;15(2):128-33. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199602000-00008. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996. PMID: 8822285
-
The role of pneumolysin in the pathogenesis of Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002 Jun;15(3):235-9. doi: 10.1097/00001432-200206000-00004. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 12015456 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased IgG but normal IgA anti-pneumococcal protein antibodies in lung of HIV-infected adults.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 2;31(35):3469-72. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.062. Epub 2013 May 10. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23664995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rapola S., Jantti V., Haikala R., Syrjanen R., Carlone G.M., Sampson J.S. Natural development of antibodies to pneumococcal surface protein A, pneumococcal surface adhesin A, and pneumolysin in relation to pneumococcal carriage and acute otitis media. J Infect Dis. 2000;182(October (4)):1146–1152. - PubMed
-
- Holmlund E., Quiambao B., Ollgren J., Nohynek H., Kayhty H. Development of natural antibodies to pneumococcal surface protein A, pneumococcal surface adhesion A and pneumolysin in Filipino pregnant women and their infants in relation to pneumococcal carriage. Vaccine. 2006;24:57–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

