Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-induced IL-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells: role of reactive oxygen species and AP endonuclease-1/redox factor (Ref)-1
- PMID: 19376732
- PMCID: PMC2846768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.03.010
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-induced IL-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells: role of reactive oxygen species and AP endonuclease-1/redox factor (Ref)-1
Abstract
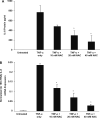
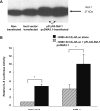
TNF-alpha contributes to oxidative stress via induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines. The molecular basis of this is not well understood but it is partly mediated through the inducible expression of IL-8. As redox factor-1 (Ref-1), is an important mediator of redox-regulated gene expression we investigated whether ROS and Ref-1 modulate TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 expression in human gastric epithelial cells. We found that TNF-alpha treatment of AGS cells enhanced nuclear expression of Ref-1 and potently induced IL-8 expression. Overexpression of Ref-1 enhanced IL-8 gene transcription at baseline and after TNF-alpha treatment whereas Ref-1 suppression and antioxidant treatment inhibited TNF-alpha-stimulated IL-8 expression. TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of other pro-inflammatory chemokines like MIP-3 alpha and Gro-alpha was also regulated by Ref-1. Although TNF-alpha increased DNA binding activity of Ref-1-regulated transcription factors, AP-1 and NF-kappaB, to the IL-8 promoter, promoter activity was mainly mediated by NF-kappaB binding. Silencing of Ref-1 in AGS cells inhibited basal and TNF-alpha-induced AP-1 and NF-kappaB DNA binding activity, but not their nuclear accumulation. Collectively, we provide the first mechanistic evidence of Ref-1 involvement in TNF-alpha-mediated, redox-sensitive induction of IL-8 and other chemokines in human gastric mucosa. This has implications for understanding the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal inflammatory disorders.
Figures
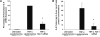




References
-
- Cooper D, Stokes KY, Tailor A, Granger DN. Oxidative stress promotes blood cell–endothelial cell interactions in the microcirculation. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2002;2(3):165–80. - PubMed
-
- Crowe SE. Helicobacter infection, chronic inflammation, and the development of malignancy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21(1):32–8. - PubMed
-
- Ernst PB, Peura DA, Crowe SE. The translation of Helicobacter pylori basic research to patient care. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(1):188–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

