Alphavbeta3-targeted nanotherapy suppresses inflammatory arthritis in mice
- PMID: 19376816
- PMCID: PMC2735365
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-129874
Alphavbeta3-targeted nanotherapy suppresses inflammatory arthritis in mice
Abstract
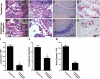
The purpose of this study was to assess whether an alternative treatment approach that targets angiogenesis, delivered through ligand-targeted nanotherapy, would ameliorate inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis was induced using the K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis. After arthritis was clearly established, mice received three consecutive daily doses of alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted fumagillin nanoparticles. Control groups received no treatment or alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted nanoparticles without drugs. Disease score and paw thickness were measured daily. Mice that received alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted fumagillin nanoparticles showed a significantly lower disease activity score (mean score of 1.4+/-0.4; P<0.001) and change in ankle thickness (mean increase of 0.17+/-0.05 mm; P<0.001) 7 d after arthritis induction, whereas the group that received alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted nanoparticles without drugs exhibited a mean arthritic score of 9.0 +/- 0.3 and mean change in ankle thickness of 1.01 +/- 0.09 mm. Meanwhile, the group that received no treatment showed a mean arthritic score of 9.8 +/- 0.5 and mean change in ankle thickness of 1.05 +/- 0.10 mm. Synovial tissues from animals treated with targeted fumagillin nanoparticles also showed significant decrease in inflammation and angiogenesis and preserved proteoglycan integrity. Ligand-targeted nanotherapy to deliver antiangiogenic agents may represent an effective way to treat inflammatory arthritis.
Figures

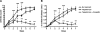

References
-
- Gartlehner G, Hansen R A, Jonas B L, Thieda P, Lohr K N. The comparative efficacy and safety of biologics for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2398–2408. - PubMed
-
- Zink A, Strangfeld A, Schneider M, Herzer P, Hierse F, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Wassenberg A, Kapelle A, Listing J. Effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis in an observational cohort study: comparison of patients according to their eligibility for major randomized clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3399–3407. - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui M A. The efficacy and tolerability of newer biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: best current evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007;19:308–313s. - PubMed
-
- Buch M H, Bingham S J, Bryer D, Emery P. Long-term infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: subsequent outcome of initial responders. Rheumatology. 2007;46:1153–1156. - PubMed
-
- Tarner I H, Muller-Ladner U, Gay S. Emerging targets of biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3:336–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

