A role for the EAL-like protein STM1344 in regulation of CsgD expression and motility in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 19376870
- PMCID: PMC2698401
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00290-09
A role for the EAL-like protein STM1344 in regulation of CsgD expression and motility in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
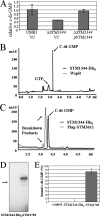
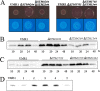
The bacterial second messenger cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) regulates the transition between sessility and motility. In Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, the expression of CsgD, the regulator of multicellular rdar morphotype behavior, is a major target of c-di-GMP signaling. CsgD expression is positively regulated by at least two diguanylate cyclases, GGDEF domain proteins, and negatively regulated by at least four phosphodiesterases, EAL domain proteins. Here, we show that in contrast to EAL domain proteins acting as phosphodiesterases, the EAL-like protein STM1344 regulated CsgD expression positively and motility negatively. STM1344, however, did not have a role in c-di-GMP turnover and also did not bind the nucleotide. STM1344 acted upstream of the phosphodiesterases STM1703 and STM3611, previously identified to participate in CsgD downregulation, where it repressed their expression. Consequently, although STM1344 has not retained a direct role in c-di-GMP metabolism, it still participates in the regulation of c-di-GMP turnover and has a role in the transition between sessility and motility.
Figures


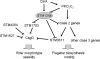
Similar articles
-
Detailed analysis of c-di-GMP mediated regulation of csgD expression in Salmonella typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Feb 2;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-0934-5. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28148244 Free PMC article.
-
Role of EAL-containing proteins in multicellular behavior of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2007 May;189(9):3613-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01719-06. Epub 2007 Feb 23. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17322315 Free PMC article.
-
Stand-Alone EAL Domain Proteins Form a Distinct Subclass of EAL Proteins Involved in Regulation of Cell Motility and Biofilm Formation in Enterobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2017 Aug 22;199(18):e00179-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00179-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28652301 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the rdar morphotype, a multicellular behaviour in Enterobacteriaceae.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Jun;62(11):1234-46. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-4557-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15818467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(11):1261-82. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.88. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25437188 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex c-di-GMP signaling networks mediate transition between virulence properties and biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028351. Epub 2011 Dec 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22164276 Free PMC article.
-
Motility control through an anti-activation mechanism in Agrobacterium tumefaciens.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Nov;116(5):1281-1297. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14823. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34581467 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed analysis of c-di-GMP mediated regulation of csgD expression in Salmonella typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Feb 2;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-0934-5. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28148244 Free PMC article.
-
Function of the Histone-Like Protein H-NS in Motility of Escherichia coli: Multiple Regulatory Roles Rather than Direct Action at the Flagellar Motor.J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(19):3110-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00309-15. Epub 2015 Jul 20. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26195595 Free PMC article.
-
C-ring requirement in flagellar type III secretion is bypassed by FlhDC upregulation.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jan;75(2):376-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06973.x. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19919668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1994. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY.
-
- Christen, M., B. Christen, M. Folcher, A. Schauerte, and U. Jenal. 2005. Identification and characterization of a cyclic di-GMP-specific phosphodiesterase and its allosteric control by GTP. J. Biol. Chem. 28030829-30837. - PubMed
-
- Cotter, P. A., and S. Stibitz. 2007. c-di-GMP-mediated regulation of virulence and biofilm formation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1017-23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

