Comparative genome-scale metabolic reconstruction and flux balance analysis of multiple Staphylococcus aureus genomes identify novel antimicrobial drug targets
- PMID: 19376871
- PMCID: PMC2698402
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01743-08
Comparative genome-scale metabolic reconstruction and flux balance analysis of multiple Staphylococcus aureus genomes identify novel antimicrobial drug targets
Abstract
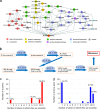
Mortality due to multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection is predicted to surpass that of human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS in the United States. Despite the various treatment options for S. aureus infections, it remains a major hospital- and community-acquired opportunistic pathogen. With the emergence of multidrug-resistant S. aureus strains, there is an urgent need for the discovery of new antimicrobial drug targets in the organism. To this end, we reconstructed the metabolic networks of multidrug-resistant S. aureus strains using genome annotation, functional-pathway analysis, and comparative genomic approaches, followed by flux balance analysis-based in silico single and double gene deletion experiments. We identified 70 single enzymes and 54 pairs of enzymes whose corresponding metabolic reactions are predicted to be unconditionally essential for growth. Of these, 44 single enzymes and 10 enzyme pairs proved to be common to all 13 S. aureus strains, including many that had not been previously identified as being essential for growth by gene deletion experiments in S. aureus. We thus conclude that metabolic reconstruction and in silico analyses of multiple strains of the same bacterial species provide a novel approach for potential antibiotic target identification.
Figures
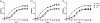
References
-
- Almaas, E., B. Kovacs, T. Vicsek, Z. N. Oltvai, and A.-L. Barabási. 2004. Global organization of metabolic fluxes in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Nature 427839-843. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya, A., S. Stilwagen, G. Reznik, H. Feil, W. Feil, I. Anderson, A. Bernal, M. D' Souza, N. Ivanova, V. Kapatral, N. Larsen, T. Los, A. Lykidis, E. J. Selkov, T. L. Walunas, A. Purcell, R. A. Edwards, T. Hawkins, R. Haselkorn, R. Overbeek, N. C. Kyrpides, and P. Predki. 2002. Draft sequencing and comparative genomics of Xylella fastidiosa subspecies reveal novel biological insights. Genome Res. 121556-1563. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

