Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 possesses a remarkable number of secretion systems
- PMID: 19376903
- PMCID: PMC2698369
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00515-09
Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 possesses a remarkable number of secretion systems
Abstract
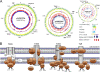
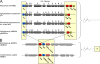
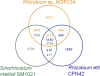
Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 is a unique alphaproteobacterium (order Rhizobiales) that forms nitrogen-fixing nodules with more legumes than any other microsymbiont. We report here that the 3.93-Mbp chromosome (cNGR234) encodes most functions required for cellular growth. Few essential functions are encoded on the 2.43-Mbp megaplasmid (pNGR234b), and none are present on the second 0.54-Mbp symbiotic plasmid (pNGR234a). Among many striking features, the 6.9-Mbp genome encodes more different secretion systems than any other known rhizobia and probably most known bacteria. Altogether, 132 genes and proteins are linked to secretory processes. Secretion systems identified include general and export pathways, a twin arginine translocase secretion system, six type I transporter genes, one functional and one putative type III system, three type IV attachment systems, and two putative type IV conjugation pili. Type V and VI transporters were not identified, however. NGR234 also carries genes and regulatory networks linked to the metabolism of a wide range of aromatic and nonaromatic compounds. In this way, NGR234 can quickly adapt to changing environmental stimuli in soils, rhizospheres, and plants. Finally, NGR234 carries at least six loci linked to the quenching of quorum-sensing signals, as well as one gene (ngrI) that possibly encodes a novel type of autoinducer I molecule.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bakkou, N., and X. Perret. 2008. Functional analysis of a second type III secretion system in Rhizobium sp. NGR234, p. 209. In M. Holsters (ed.), Abstract book of the Eighth European Nitrogen Fixation Conference, Ghent, Belgium.
-
- Becker, A., N. Fraysse, and L. Sharypova. 2005. Recent advances in studies on structure and symbiosis-related function of rhizobial K-antigens and lipopolysaccharides. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 18:899-905. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., A. Kleickmann, H. Kuster, M. Keller, W. Arnold, and A. Pühler. 1993. Analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti genes exoU, exoV, exoW, exoT, and exoI involved in exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and nodule invasion: exoU and exoW probably encode glucosyltransferases. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 6:735-744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

